Los trabajos sobre anemia en la insuficiencia cardíaca (IC) tienden a aceptar la anemia como una disfunción cardiorrenal combinada, sin realizar estudios etiológicos, omitiendo su carácter sindrómico. Nuestro objetivo es conocer el perfil etiológico y el tratamiento de la anemia en la IC en el medio hospitalario.
Pacientes y métodoAnálisis transversal inicial de una cohorte multicéntrica de pacientes con IC y anemia recogidos de forma prospectiva. Utilizamos los criterios de la Organización Mundial de la Salud (OMS) para definir anemia, la ecuación Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) para el cálculo del filtrado glomerular y unos criterios comunes para definir la etiología de la anemia.
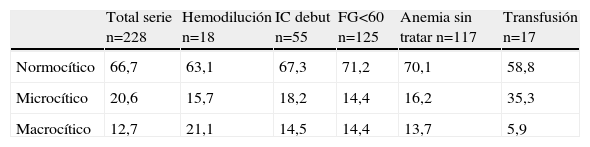
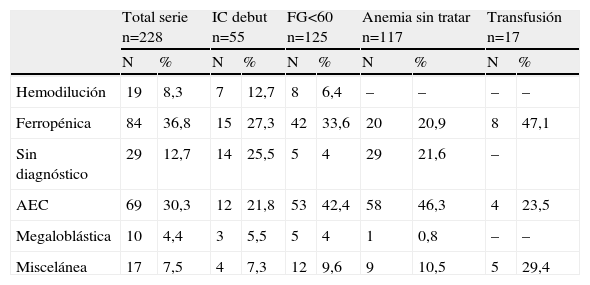
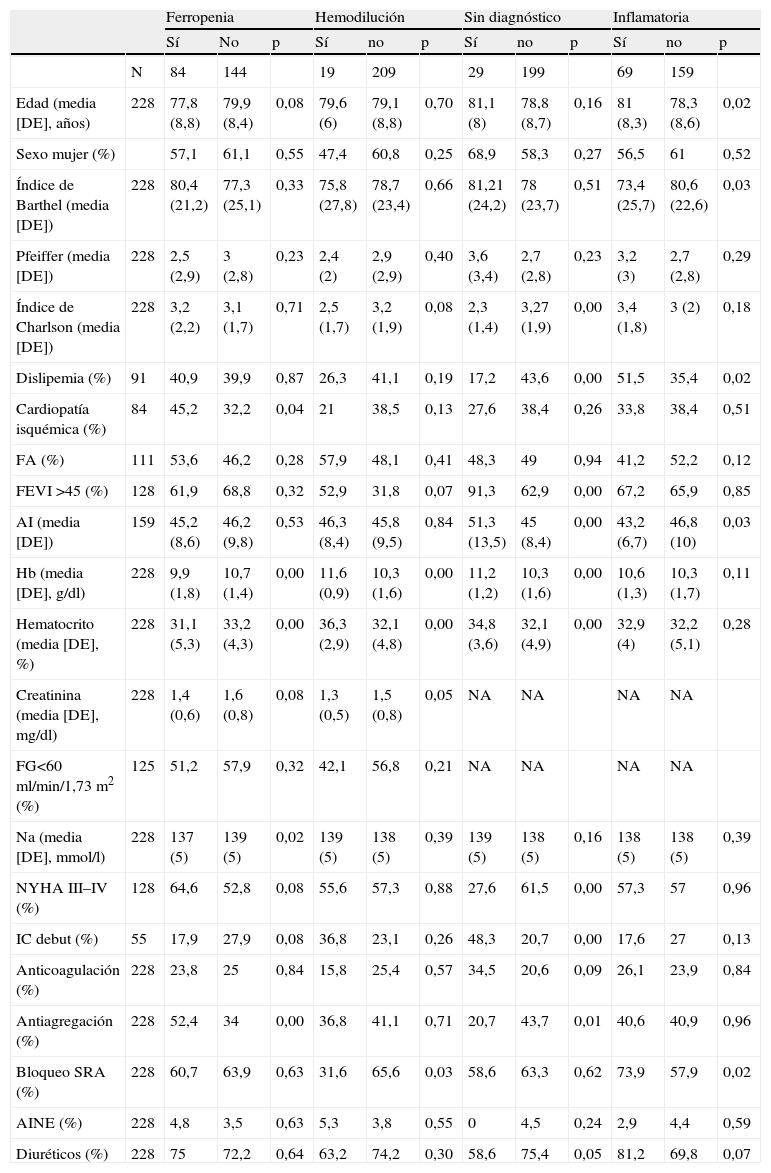
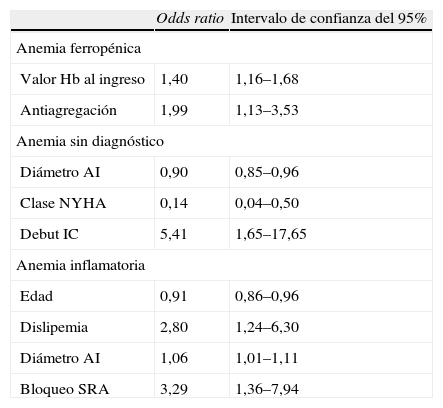
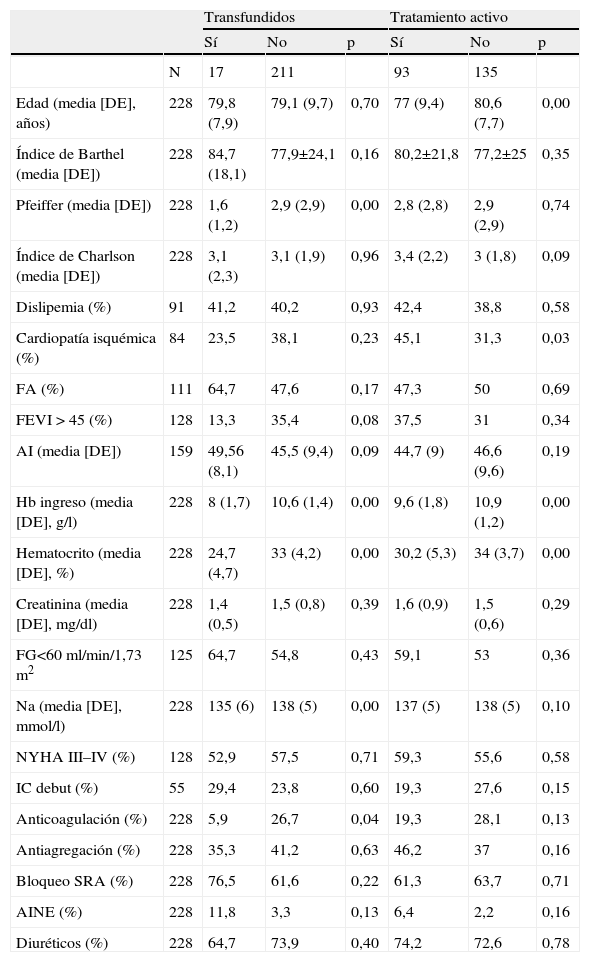
ResultadosSe incluyó a 228 pacientes, con edad media de 79,1 años, y el 59,65% mujeres. El 36,8% tenía anemia ferropénica y el 30,3% anemia de enfermedad crónica. En el 12,7% de los casos no se llegó a ningún diagnóstico etiológico. La variable con mayor potencia asociada a anemia ferropénica fue el tratamiento previo con antiagregantes (odds ratio [OR]=1,99; intervalo de confianza [IC] del 95%, 1,13–3,53) y para anemia de enfermedad crónica, los bloqueadores del sistema renina angiotensina (SRA) (OR=3,29; IC del 95%, 1,36–7,94). La anemia sin diagnóstico se asociaba con IC en su inicio (OR=5,41; IC del 95%, 1,65–17,65). Recibió transfusión el 8,1% de los pacientes; un 6%, eritropoyetina, y el 25,3%, suplementos de hierro. La edad (OR=1,04; IC del 95%, 1–1,08) y un valor más bajo de hemoglobina al ingreso (OR=1,81; IC del 95%, 1,46–2,25) determinaron una actitud activa de tratamiento.
ConclusionesUn protocolo clínico de estudio de la anemia en la IC permite en un 70% de los casos un diagnóstico etiológico y un tratamiento más eficaz.
Studies about anemia in heart failure (HF) tend to link the anemia to a cardio-renal dysfunction, and its syndromic value is seldom evaluated. Our objective was to assess the etiology and clinical management of anemia in HF patients in a hospital setting.
Patients and methodInitial cross-sectional analysis of a multi-center and prospective cohort of patients with HF and anemia. Anemia was defined according to the WHO criteria; the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease equation was used to assess glomerular filtration and the etiology of anemia was defined according to common criteria.
ResultsWe evaluated 228 patients, with a median age of 79.1 years and 59.65% women. Iron deficiency anemia was present in 36,8% of patients and anemia of chronic disease in 30.3%. Of note, 12.7% cases did not meet any etiological criteria. The main factor associated with iron deficiency was anti-platelet therapy (OR=1.99; 95% CI, 1.16–1.68) and the main factors associated with anemia of chronic disease were the use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) or angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARA-II) (OR=3.29; 95% CI, 1.36–7.94). The main factor associated with undefined anemia was initial heart failure (OR=5.41; 95% CI, 1.65–17.65). On the other hand, 8.1% of patients required transfusion, 6% were treated with erythropoietin and 25.3% were treated with iron. Both age (OR=1.04; 95% CI, 1–1.08) and hemoglobin level at admission (OR=1.81; 95% CI, 1.46–2.25) were associated with active treatment for anemia.
ConclusionsA clinical study of anemia in patients with HF can establish an etiological diagnosis in 70% of cases, resulting in a more effective treatment.