Journal Information
Vol. 125. Issue 8.
Pages 281-285 (September 2005)
Vol. 125. Issue 8.
Pages 281-285 (September 2005)
DOI: 10.1157/13078420
Actividad de la tiopurina metiltransferasa en la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. Un estudio en 7.046 pacientes españoles
Thiopurine methyltransferase activity in the inflammatory bowel disease. A study on 7046 Spanish patients
Visits
16438
Javier P Gisberta, Fernando Gomollónb, Carlos Carac, Marta Lunaa, Yago González-Lamaa, José María Pajaresa, José Matéa, Luis G Guijarrod
a Servicio de Aparato Digestivo. Hospital Universitario de la Princesa. Universidad Autónoma. Madrid.
b Servicio de Aparato Digestivo. Hospital Clínico Universitario. Zaragoza.
c Departamento Médico. UCB-Celltech Pharma. Madrid.
d Unidad de Toxicología Molecular Hepática. Departamento de Bioquímica y Biología Molecular. Universidad de Alcalá. Alcalá de Henares. Madrid. España.
This item has received
Article information
Abstract
Full Text
Bibliography
Download PDF
Statistics
Tables (4)
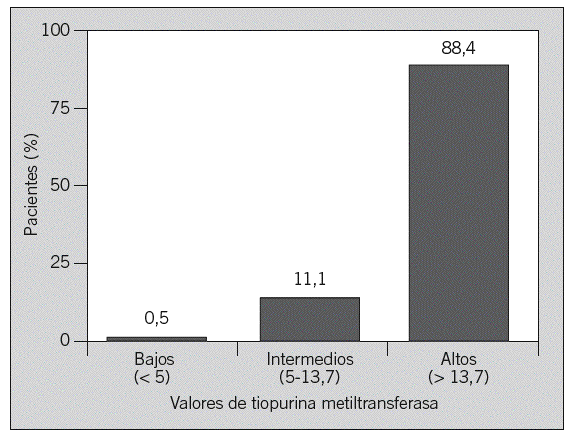
Fig. 1. Distribución de los pacientes en función de los valores de tiopurina metiltransferasa (U/ml) categorizados como bajos, intermedios y altos.
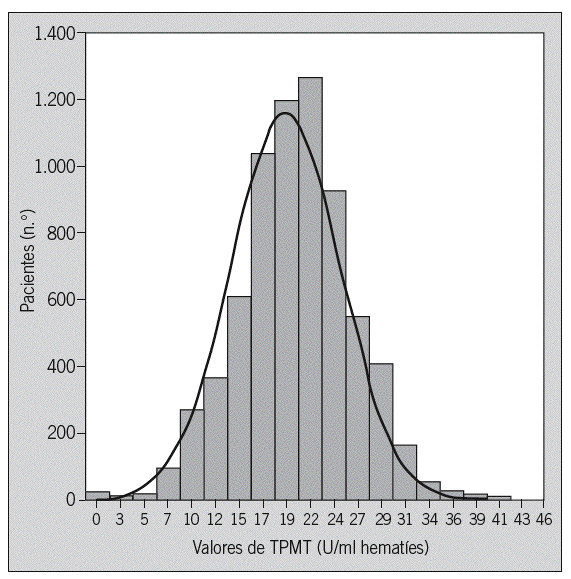
Fig. 2. Distribución de los valores de tiopurina metiltransferasa en la población estudiada.
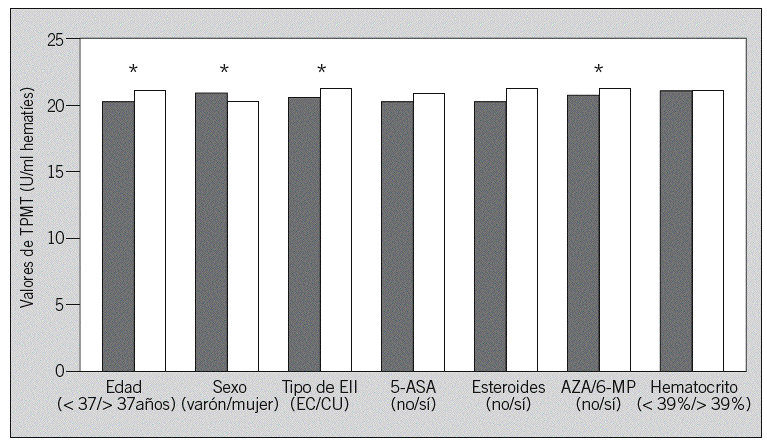
Fig. 3. Valores de tiopurina metiltransferasa (TPMT) en función de las variables consideradas en el estudio. EII: enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal; EC: enfermedad de Crohn; CU: colitis ulcerosa; 5-ASA: 5-aminosalicílicos; AZA: azatioprina; 6-MP: mercaptopurina. *p < 0,001.
Show moreShow less
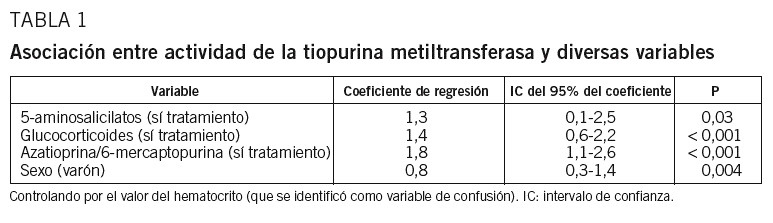
Fundamento y objetivo: El objetivo del presente estudio es describir la actividad enzimática de la tiopurina metiltransferasa (TPMT) en un grupo muy numeroso de pacientes españoles con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal (EII), evaluar el efecto de algunas variables sobre dicha actividad y conocer la proporción de pacientes con baja actividad y, por tanto, mayor riesgo de mielotoxicidad por azatioprina/6-mercaptopurina. Pacientes y método: Se determinó la actividad de TPMT mediante un método radioquímico en pacientes con EII. La asociación entre diversas variables y la actividad de TPMT se estudió mediante regresión lineal múltiple. Resultados: Se incluyó a 7.046 pacientes, el 70% con enfermedad de Crohn, el 22% con colitis ulcerosa y un 8% con colitis indeterminada. El valor medio de TPMT fue de 20 U/ml (extremos: 0-46). La distribución de actividad de TPMT fue: un 0,5% con valores bajos (< 5 U/ml), un 11,1% con valores intermedios (5-13,7) y un 88,4% con valores altos (>= 13,8). Los valores de TPMT no siguieron una distribución normal (p < 0,001). En el estudio univariante se demostraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas (p < 0,001), aunque de dudosa relevancia clínica al ser mínimos, en los valores de TPMT en función de la edad, el sexo, el tipo de enfermedad y el tratamiento con azatioprina/6-mercaptopurina. En el estudio multivariante, el sexo y el tratamiento con 5-aminosalicilatos, glucocorticoides y azatioprina/6-mercaptopurina se asoció significativamente con la actividad de TPMT. Conclusiones: El 0,5% de los pacientes españoles con EII tiene una baja actividad enzimática de TPMT (< 5 U/ml, lo que indica un mayor riesgo de mielotoxicidad por azatioprina/6-mercaptopurina), una cifra similar a la descrita en otros países. Los diversos fármacos empleados en el tratamiento de la EII, como los 5-aminosalicilatos o la azatioprina/6-mercaptopurina, no parecen modificar de forma clínicamente relevante dicha actividad enzimática.
Palabras clave:
Enfermedad de Crohn
Colitis ulcerosa
Enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal
Azatioprina
6-mercaptopurina
Tiopurina metiltransferasa
Background and objective: Our objective was to assess the activity of thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) in a very large number of Spanish patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), to evaluate the influence of several variables (including azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine) on that activity, and to know the proportion of patients with low TPMT activity and therefore high risk of myelotoxicity when treated with these drugs. Patients and method: TPMT activity in red blood cells (RBCs) was measured by a radiochemical method. The association between several variables and TPMT values was assessed by multiple lineal regression. Results: 7046 patients were included (mean age: 37 years; 53% males): 70% with Crohn's disease, 22% with ulcerative colitis, and 8% with indeterminate colitis. Mean TPMT value was 20 (6) U/ml RBCs (minimum 0 and maximum 46). TPMT activity distribution was as follows: low levels (< 5 U/ml), 0.5%; intermediate (5-13.7), 11.1%; and high (>= 13.8), 88.4%. TPMT values did not follow a normal distribution (p < 0.001). In the univariate study, statistically significant differences (p < 0.001), yet of doubtly clinical significance because its minimal magnitude, were demonstrated in TPMT values depending on age, sex, type of disease, and treatment with azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine. In the multivariate study, the variables associated with TPMT activity were: sex, treatment with 5-aminosalicylates, steroids and azathioprine/6-mercaptopurine. Conclusions: This study shows that 0.5% of the Spanish patients with IBD have low TPMT activity (< 5 U/ml RBCs), a figure similar to that reported in other countries, these patients being at higher risk of myelotoxicity when treated with azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine. The drugs usually prescribed for the treatment of IBD, including 5-aminosalicylates and azathioprine/6-ercaptopurine, do not seem to modify in a clinically relevant manner TPMT activity.
Keywords:
Crohn's disease
Ulcerative colitis
Inflammatory bowel disease
Azathioprine
6-mercaptopurine
Thiopurine methyltransferase
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Medicina Clínica
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail