La infección de localización quirúrgica es una de las principales causas de infección relacionada con la asistencia sanitaria. Una de las medidas más habituales para su reducción es la preparación prequirúrgica. El objetivo de este estudio fue medir el grado de adecuación al protocolo prequirúrgico en los pacientes sometidos a cirugía cervical y su relación con la incidencia de infección de localización quirúrgica.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional de cohortes realizado desde enero de 2011 a diciembre de 2017. Se recogieron variables relacionadas con el paciente, la preparación prequirúrgica y la infección. Se calculó la incidencia de infección tras un período máximo de 30días tras la cirugía. Se evaluó la asociación entre la adecuación al protocolo de preparación prequirúrgica y la presencia de infección.
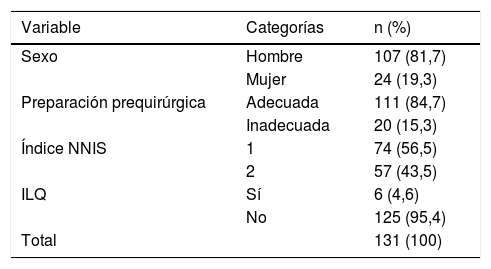
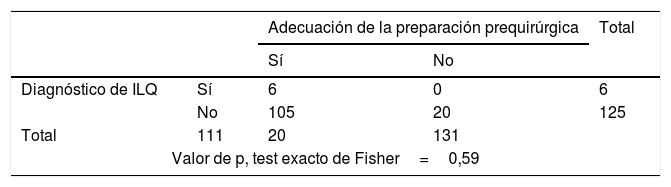
ResultadosEl estudio incluyó 131 pacientes. La adecuación global al protocolo de preparación prequirúrgica fue del 84,7%, siendo la causa más frecuente de inadecuación la aplicación del colutorio (7,6% de las intervenciones). La incidencia global de infección de localización quirúrgica durante el periodo de seguimiento fue del 4,6% (IC95%: 1,0-8,2%). No se encontró relación entre la adecuación al protocolo y la presencia de infección (p=0,59).
ConclusionesLa adecuación de la preparación prequirúrgica en nuestro hospital fue alta y la incidencia de infección de localización quirúrgica baja, no encontrándose relación entre ambas. De los resultados se desprende una elevada cultura en seguridad en esta cirugía. No obstante, aún existe margen de mejora en la calidad asistencial de nuestros pacientes.
Surgical wound infection is one of the leading causes of healthcare-associated infections. One of the most common measures for its reduction is the pre-surgical preparation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the adequacy to the pre-surgical protocol in patients undergoing neck surgery and the relationship with the incidence of surgical wound infection.
Material and methodsObservational cohort study, conducted from January 2011 to December 2017. Variables related to patient, pre-surgical preparation and infection were collected. Infection rate was calculated after a maximum period of 30days after surgery. The effect of the pre-surgical preparation's adequacy and infection was evaluated.
ResultsThe study included 131 patients. The global adequacy of the pre-surgical protocol was 84.7%, being the main cause of inadequacy the application of the mouthwash (7.6% of the interventions). The overall incidence of surgical wound infection during the follow-up period was 4.6% (95%CI: 1.0%-8.2%). No relationship between the adequacy to the protocol and the presence of infection was found (P=.59).
ConclusionsAdequacy of the pre-surgical preparation in our hospital was high and the incidence of surgical wound infection was low, and no relationship was found between the two. The results show a high safety culture in this surgery. However, there is still room for improvement in the quality of care of our patients.