El sistema endotelina, por su acción vasoconstrictora, participa en el desarrollo de hipertensión arterial esencial (HTAe). El análisis del polimorfismo de sus genes representa un nuevo enfoque en el estudio de esta enfermedad. Propusimos analizar la interacción entre ins/del A los estadios de HTAe y factores de riesgo con los polimorfismos 138ex1 del gen de endotelina-1 (ET-1) y H323H del gen del receptor A de ET-1 (ETRA).
Pacientes y métodosSe analizó a 300 pacientes de ambos sexos, no parentales, que asistieron en forma consecutiva al consultorio de hipertensión arterial. Se les realizó un examen físico completo, electrocardiograma, ecocardiograma, y Rx de tórax. Se determinaron los polimorfismos mediante amplificación seguida con corte con enzimas de restricción a partir de ADN aislado de sangre periférica.
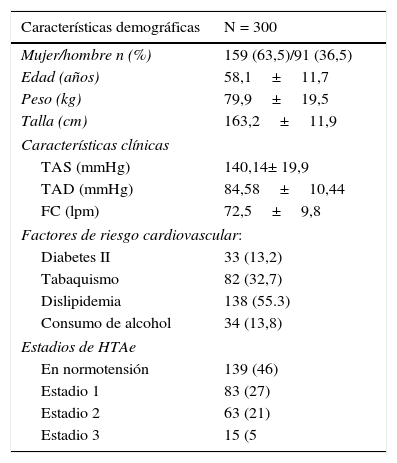
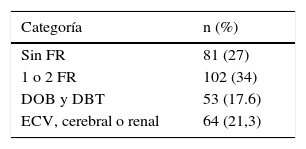
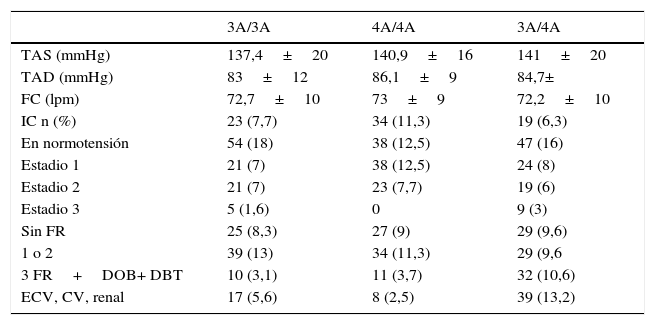
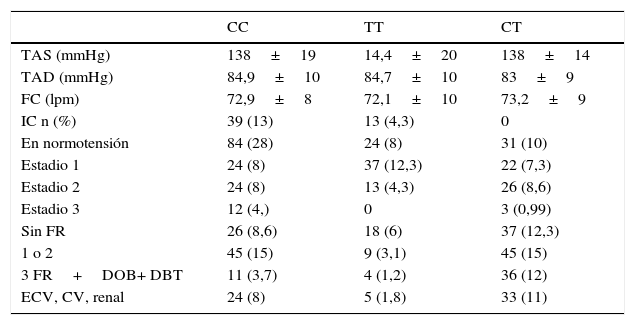
ResultadosEl 46% de los pacientes tuvieron HTAe controlada, el 17,6% presentaron daño de órgano blanco o enfermedad cardiovascular, cerebral o renal. Se observó que los portadores del genotipo 4A/4A del polimorfismo 138ex1 ins/del A del gen de ET-1 mostraron menor frecuencia de enfermedad cardiovascular, renal y cerebral (p<0,032; IC 95%: 11,1-21,4). Para el polimorfismo H323H, la evaluación por imágenes mostró mayor frecuencia de dilatación de aurícula izquierda (p=0,02) y fibrilación auricular (p=0,03) entre los portadores T/T, y entre los C/C mayor frecuencia de cardiomegalia (p=0,04).
ConclusiónLos genotipos 4A/4A del gen de ET-1 y el T/T del gen de ETRA podrían participar agravando el daño cardiovascular. Su identificación contribuiría a reconocer subgrupos de pacientes con diferente riesgo.
The endothelin system, for its vasoconstrictor action, is related to the development of essential hypertension (HTAe). The polymorphism analysis of their genes represents a new approach to the study of this disease. We propose to analyze the interaction between stages of essential hypertension (HTAe) and risk factors with polymorphisms 138ex1 ins/del A gene endothelin-1 (ET-1) and H323H receptor gene A ET-1 (ETRA).
Patients and methodsWe included 300 patients of both sexes, unrelated, who consecutively attended the clinic hypertension medical service. Each one underwent a complete physical examination, electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and Rx thorax. The degree of severity of hypertension was determined in stages. The determination of polymorphisms was performed by amplification followed by cutting by specific restriction enzyme from DNA obtained from peripheral blood.
ResultsThe 46% of patients had HTAe controlled, 17.6% had organ damage or cardiovascular, brain or kidney disease. It was observed that the 4A/4A carriers showed lower frequency of cardiovascular disease, kidney and brain (P<.032; 95% CI: 11.1-21.4). For H323H polymorphism, the evaluation by images showed a higher frequency of the dilations of left auricular (P=.02) and auricular fibrillation (P=.03) between the T/T carrier, a higher frequency of cardiomegaly was detected in C/C patients (P=.04).
ConclusionThe genotypes, 4A/4A of the ET-1 gene and the T/T from ETRA gene might be involved in worse outcome of cardiovascular damage. Their identification could help recognize subgroups of the hypertensive patients with different risk.