Acute pancreatitis is a common cause of acute abdomen in pregnant women. The purpose of this study was to determine the frequency at our institution and its management and outcomes.
MethodsA retrospective analysis of a database of cases presented in 7 consecutive years at a tertiary center was performed.
ResultsBetween December 2002 and August 2009, there were 19 cases of acute pancreatitis in pregnant women, 85% with a biliary etiology. The highest frequency was in the third trimester of pregnancy (62.5% cases). In cases of gallstone pancreatitis, 43.6% of pregnant women had previous episodes before pregnancy. A total of 52.6% of the patients were readmitted for a recurrent episode of pancreatitis during their pregnancy. Overall, 26.3% of the patients received antibiotic treatment and 26.3% parenteral nutrition. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy was performed during the 2nd trimester in two patients (10.5%). There was no significant maternal morbidity.
ConclusionAcute pancreatitis in pregnant women usually has a benign course with proper treatment. In cases of biliary origin, it appears that a surgical approach is suitable during the second trimester of pregnancy.
La pancreatitis aguda es causa frecuente de abdomen agudo en gestantes. El objetivo era conocer la frecuencia en nuestro centro, así como su manejo y resultados.
MetodologíaAnálisis retrospectivo de los casos presentados en 7 años consecutivos, buscando en la base de datos de un centro de tercer nivel.
ResultadosEntre diciembre de 2002 y agosto del 2009, hubo 19 casos de pancreatitis aguda en gestantes, el 85% de ellos de etiología biliar. La mayor frecuencia era en el tercer trimestre (62,5% casos). En los casos de pancreatitis litiásica, el 43,6% de las gestantes habían presentado episodios previos al embarazo. El 52,6% reingresaron por una recidiva del episodio de pancreatitis. Recibieron tratamiento antibiótico el 26,3%, y nutrición parenteral otro 26,3%. Se intervino de colecistectomía laparoscópica durante el segundo trimestre a 2 pacientes (10,5%). No hubo morbimortalidad maternoinfantil significativa.
ConclusiónLa pancreatitis en gestantes suele tener una evolución benigna con el tratamiento adecuado. En los casos de origen biliar, parece seguro intervenir durante el segundo trimestre de gestación.
Acute pancreatitis is a relatively common disease in pregnant women (1/1500–4500 pregnancies), and most are gallstone related (70%) due to hormonal lithogenic effects.1 Similarly, other causes, such as hypertriglyceridemia (20%), and other less common, such as hyperparathyroidism, autoimmunity or toxic elements can trigger acute pancreatitis symptoms in pregnant women. Its progression can be fatal; fetal losses of up to 4.7% were documented in a series of 34 cases.1
Our review aimed to determine epidemiology of acute pancreatitis in pregnant women, the treatment performed and outcome in terms of associated maternal and infant morbidity and mortality at our center.
Patients and MethodWe performed a retrospective study from December 2002 to August 2009, using searches for diagnoses with the terms “pregnancy”, “pregnant”, “pancreatitis” in our hospital's CIM-9 database. We reviewed written and electronic medical records, and we tried to contact patients by telephone for whom no study data was available in order to gather information. We performed a descriptive data analysis, including: affiliation, pregnancy status, diagnostic tests, staging pancreatitis severity with the Ransom2 scale or the Balthazar3 score, clinical changes, surgical intervention and termination of pregnancy.
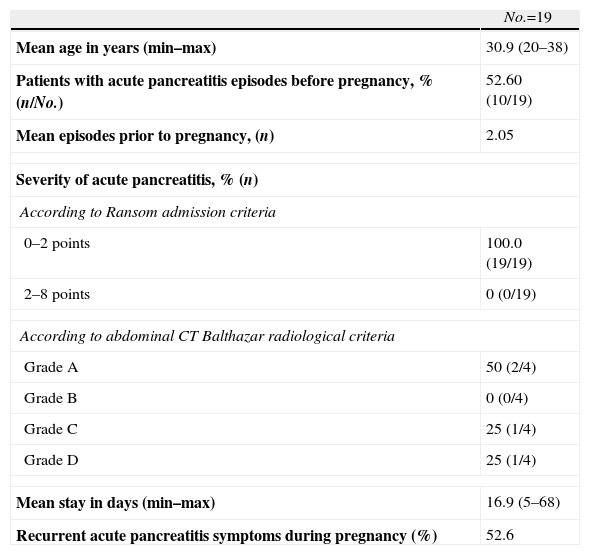
ResultsFrom December 2002 to August 2009, a total of 16549 births were recorded in our center. However, only 19 patients were reported with acute pancreatitis episodes, representing 1.15/1000 pregnancies. The total of acute pancreatitis, according to the database, in that period was 1778 cases, which means that acute pancreatitis in pregnant women was 1.06%. The data obtained are listed in Table 1. Pancreatitis symptoms occurred mostly during the third trimester (52.65%). The most common was biliary etiology in 85% of cases (16/19). For the remaining 15%, a secondary case was attributed to hyperlipidemia, one idiopathic and another possibly of biliary origin (patient with pre-pregnancy cholecystectomy). Likewise, it was found that 100% of pregnant women who had an acute pancreatitis episode during the first trimester of pregnancy, were later readmitted for the same reason. However, patients who experienced an acute pancreatitis episode in the second or third trimesters had a relapse in 50% of cases during pregnancy. One patient suffered acute pancreatitis overlapped with delivery and the immediate postpartum period. Overall, we found that 52.6% of patients were readmitted to our hospital for recurrence of pancreatitis episodes.
Data on the Patients Studied.
| No.=19 | |
| Mean age in years (min–max) | 30.9 (20–38) |
| Patients with acute pancreatitis episodes before pregnancy, % (n/No.) | 52.60 (10/19) |
| Mean episodes prior to pregnancy, (n) | 2.05 |
| Severity of acute pancreatitis, % (n) | |
| According to Ransom admission criteria | |
| 0–2 points | 100.0 (19/19) |
| 2–8 points | 0 (0/19) |
| According to abdominal CT Balthazar radiological criteria | |
| Grade A | 50 (2/4) |
| Grade B | 0 (0/4) |
| Grade C | 25 (1/4) |
| Grade D | 25 (1/4) |
| Mean stay in days (min–max) | 16.9 (5–68) |
| Recurrent acute pancreatitis symptoms during pregnancy (%) | 52.6 |
CT: computerized tomography.
The average stay of patients was 16.9 days per acute pancreatitis episode.
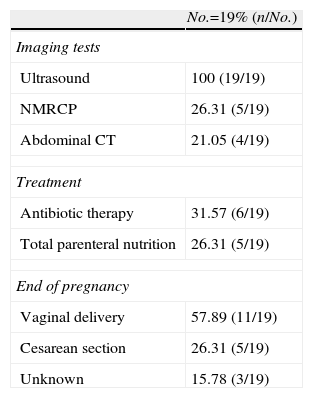
Diagnostic MethodsFor all cases, diagnosis of acute pancreatitis was clinical and analytical; the mean serum amylase at diagnosis was 1091IU/l (range: 181–4600IU/l). Imaging methods used for the diagnosis and staging of severity included abdominal ultrasound, nuclear magnetic resonance cholangiography (NMRCP) and abdominal computed tomography (CT). Abdominal ultrasound was performed in 100% of patients. 26% of pregnant women also underwent NMRCP. 21% of patients (not coincident with the NMRCP) also underwent abdominal CT; all cases were in the third trimester of pregnancy, and patients with the worst general condition. These data are shown in Table 2.
Results of Diagnostic Testing, Treatment, and End of Pregnancy of the Patients.
| No.=19% (n/No.) | |
| Imaging tests | |
| Ultrasound | 100 (19/19) |
| NMRCP | 26.31 (5/19) |
| Abdominal CT | 21.05 (4/19) |
| Treatment | |
| Antibiotic therapy | 31.57 (6/19) |
| Total parenteral nutrition | 26.31 (5/19) |
| End of pregnancy | |
| Vaginal delivery | 57.89 (11/19) |
| Cesarean section | 26.31 (5/19) |
| Unknown | 15.78 (3/19) |
NMRCP: nuclear magnetic resonance cholangiography; CT: computed tomography.
To classify the acute pancreatitis episode, the Ransom4 scale was used at admission (age >55; leukocytosis >16000/mL; glycemia >200mg/dL; GOT >250IU/mL; LDH >350IU/mL), and applied again at 48h. (hematocrit drop >10%; increase in urea >1.8mg/dL; calcemia <8mg/dL; pO2 <60mmHg), finding that the score on admission was ≤2 in all cases (mortality <0.9%), and at 48h, it was =0 in 94.7% of cases. For cases where CT was performed (21%), we found Balthazar grade A (normal pancreas) pancreatitis in 2 patients, grade C (peripancreatic inflammation) in one patient and Grade D (pancreatic collection) in another pregnant patient.
TreatmentAntibiotic treatment was administered to 31.57% (7/19) of patients, all in the second and third trimesters, with clear indication in only 3 cases: one suspected associated cholecystitis, one case of acalculous pancreatitis with parenteral feeding catheter-related bacteremia, and one case of grade D pancreatitis by abdominal CT according to Balthazar classification. Total parenteral nutrition was administered in 26.3% (5/19) of patients. Three patients matched both treatment regimens (Table 2). Only one patient required admission to the critical care unit (the patient who developed catheter-related bacteremia).
Surgical treatment involved 3 laparoscopic cholecystectomies during pregnancy, all in the second trimester (week 19 and week 23 at our center by laparoscopic approach, and at week 20 at another hospital). No postoperative complications occurred in the pregnant women who underwent surgery. Cases were treated medically in the first and third trimesters. One patient underwent surgery in the immediate postpartum (third day), and 6 other patients after this period. Of the remaining patients, 5 cases have yet to undergo cholecystectomy, and 3 patients are unreachable. A pregnant woman admitted for acute pancreatitis had undergone cholecystectomy.
Fetal Morbidity and MortalityFetal morbidity and mortality was zero (0%) in the surgical patients, prior to pregnancy, during pregnancy, and during the postpartum period.
57.9% of pregnant women (11/19) had normal deliveries at the end of their pregnancy. However, 26.3% (5/19) required a cesarean: 3 patients for suspected fetal distress; one for failure at induction at 41 weeks of pregnancy, and one case of placental abruption and eclampsia. Fetal outcome was correct for all cesarean sections. One case in one of the normal deliveries had low weight for the gestational age. Despite all attempts and methods to locate patients, the final result of pregnancy for 3 cases (Table 2) is unknown.
DiscussionOur center is a referral hospital for a specific population and geographical area, where a variety of patients are referred from different areas, including pregnant women with surgical abdominal disease.
Pregnant women suffering acute pancreatitis represent a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge, because a delay in diagnosis and treatment can have serious implications for maternal–fetal viability.5 Pancreatitis in pregnant women has occurred in 1.15/1000 pregnancies recorded at our center. One of the important aspects of acute pancreatitis in pregnant women is the repetition of the same episode during pregnancy. The risk of recurrence of acute pancreatitis is high, but similar to those discussed in previous studies; in our series, 52.6% of patients presented it. Swisher et al.6 described a recurrence risk of 92% for the first trimester, 64% in the second, and 44% in the third, with 50% overall for pancreatitis. Duphar7 indicated 23% of readmissions. Possibly, this fact would raise the need for a CL during pregnancy.
For the diagnosis of pancreatitis, clinical history and elevated blood parameters, such as pancreatic amylase, are mandatory.5 Abdominal ultrasound is a good test to detect sludge and stones in the gallbladder, but not in the bile duct, to protect the fetus or embryo from irradiation. One modality, such as endoscopic ultrasound (scan under sedation), has a predictive value close to 100%, but has not been used at our center; we use NMRCP instead. Abdominal CT is widely used to obtain the pancreatitis severity index under the Balthazar score, but is not recommended for pregnant women, due to ionizing radiation.8 However, for 21% of our pregnant women, CT was performed outside the fetal organogenesis period (first trimester). Some studies have pointed out the importance of classifying acute pancreatitis by the abdominal CT-generated images. In our patients, most episodes were mild pancreatitis without glandular necrosis.
An important mode of treatment for acute pancreatitis is electrolyte replacement with or without antibiotics. In our series, although in most cases the degree of acute pancreatitis was mild, antibiotic therapy was administered to 31.57% of patients; it was only recommended for documented superinfection cases.9,10
Given the number of recurrences of acute pancreatitis in pregnant women, especially those which are diagnosed in the first trimester, the multidisciplinary team treating them must consider surgery as an alternative to the possible recurrence of unforeseeable consequences. The best time for surgery is the second trimester (13–26 weeks), because the risk of abortion or preterm delivery is less than 5%. During the first trimester, possible effects of drugs used during patient anesthesia may eventually impair fetal organogenesis and produce up to 12% of abortions. Some caution is required in these cases. During the third trimester, 40% of patients may experience unexpected labor.11
Recommendations include taking into account that 52.60% of patients with gallstone pancreatitis had experienced episodes before pregnancy, and that new episode risk reduction after cholecystectomy (from 76% to 5%) is known11,12; common sense indicates the benefit of surgery for young women who desire pregnancy.
At our hospital, we have not had the need to perform other procedures to treat acute biliary pancreatitis, such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (our guidelines and those of other sites only recommend it for choledocholithiasis cases)12 or cholecystostomy (ultrasound-guided percutaneous or surgical), or nasobiliary drainage.13,14
Given that this study is a retrospective analysis, it carries some limitations, because some cases have been lost to follow-up, and after several telephone attempts to contact the patients, we have been unable to find out the end of pregnancy outcome or if these patients underwent laparoscopic cholecystectomy surgery.
ConclusionAcute pancreatitis in pregnant women has a clinical course with low morbidity and mortality. The most common cause is gallstones. There is a high rate of episode recurrence during pregnancy, implying a need to assess the patient and to propose an LC in selected cases during pregnancy.
Conflict of InterestNone.
Please cite this article as: Vilallonga R, Calero-Lillo A, Charco R, Balsells J. Pancreatitis aguda durante la gestación, experiencia de 7 años en un centro de tercer nivel. Cir Esp. 2014;92:468–471.