Simultaneous pancreas–kidney transplantation (SPKT) constitutes the therapy of choice for diabetes type 1 or type 2 associated with end-stage renal disease, because is the only proven method to restore normo-glicemic control in the diabetic patient.
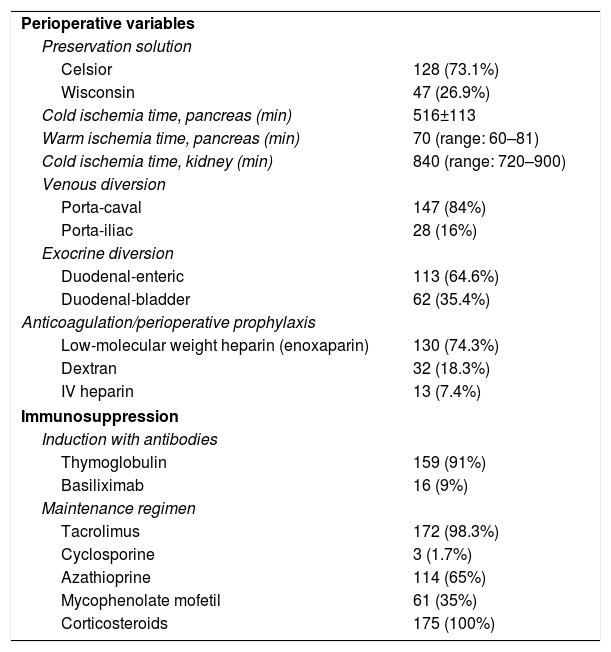
MethodsRetrospective and descriptive study of a series of 175 patients who underwent SPKT from March 1995 to April 2016. We analyze donor and recipient characteristics, perioperative variables and immunosuppression, post-transplant morbi-mortality, patient and graft survival, and risk factors related with patient and graft survival.
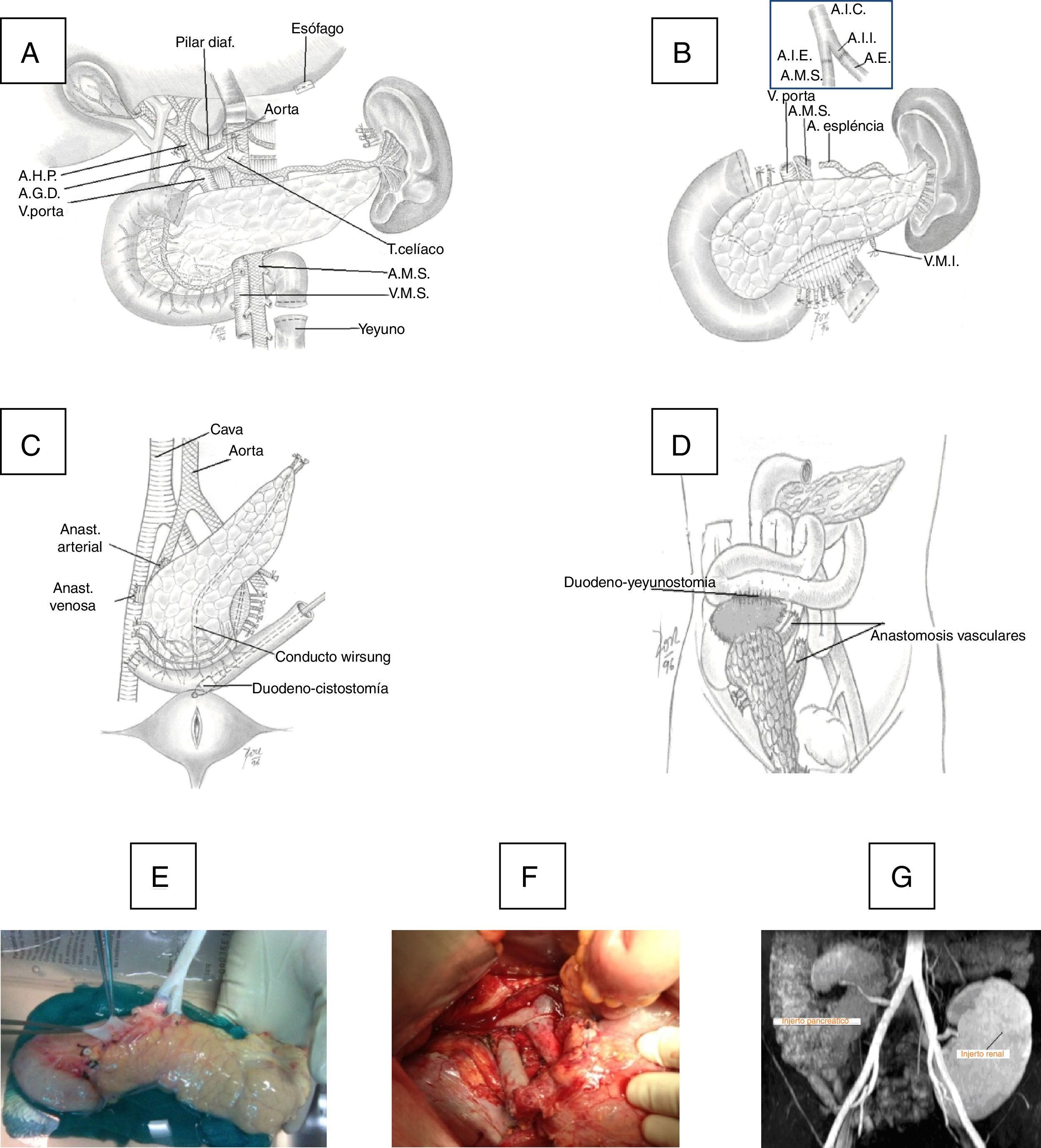
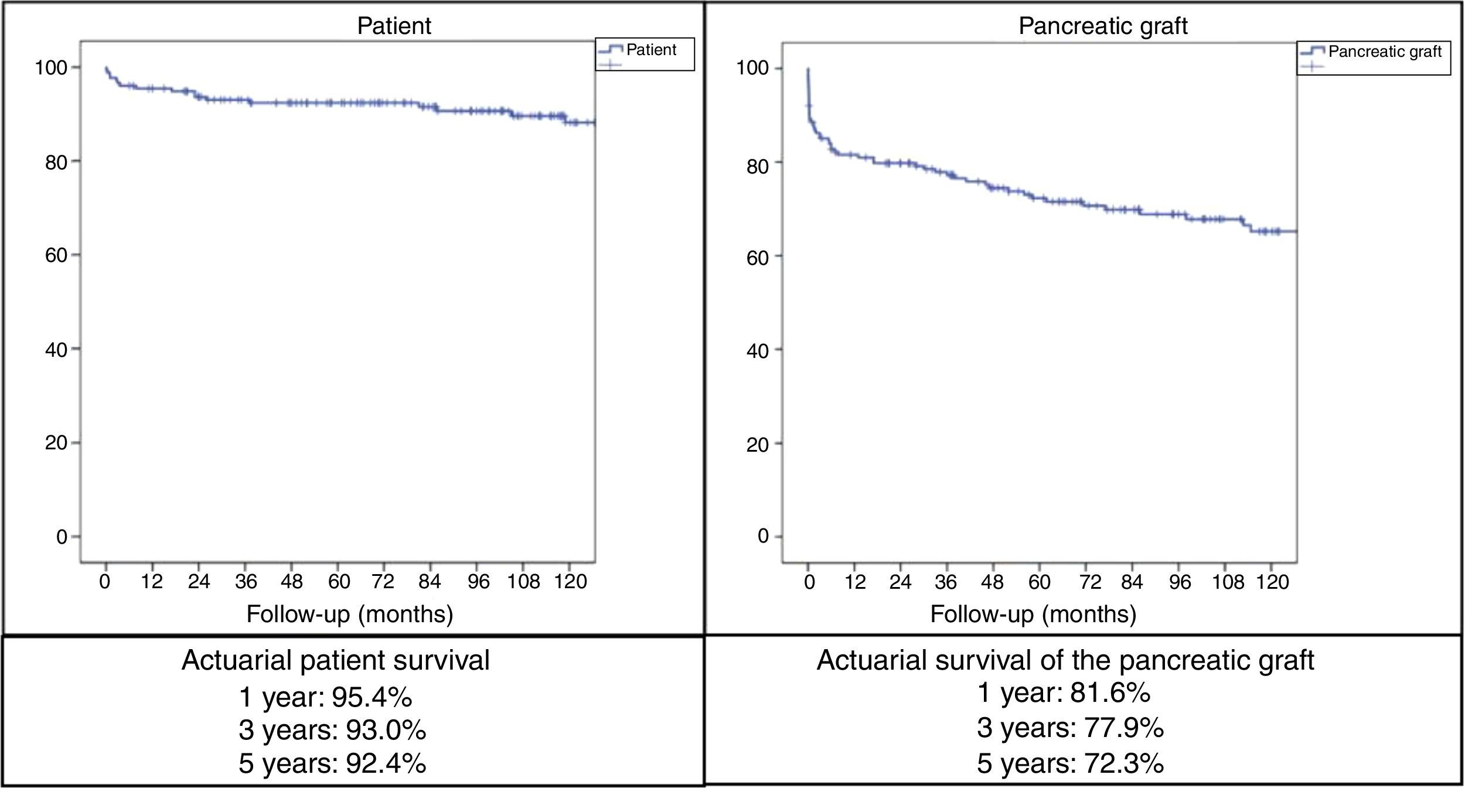
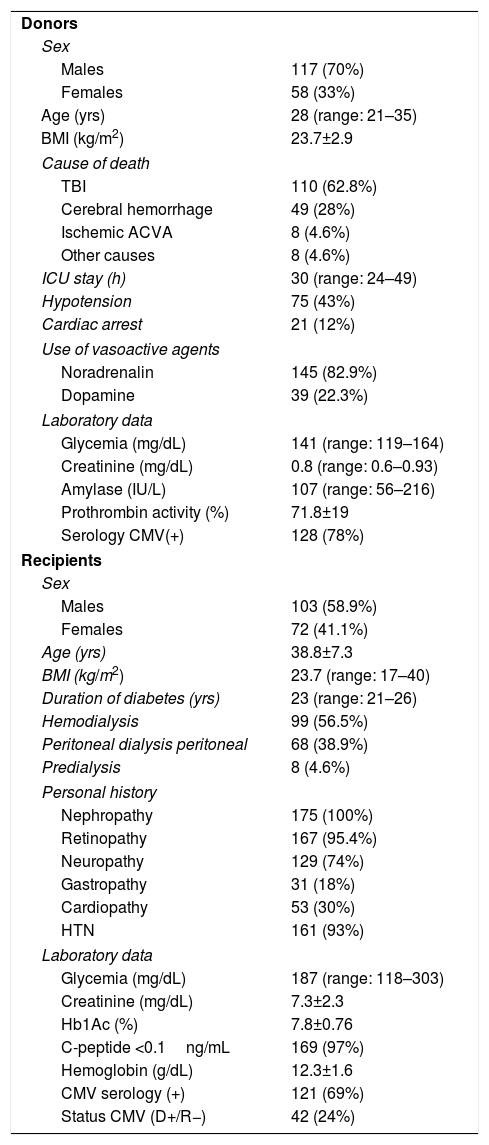
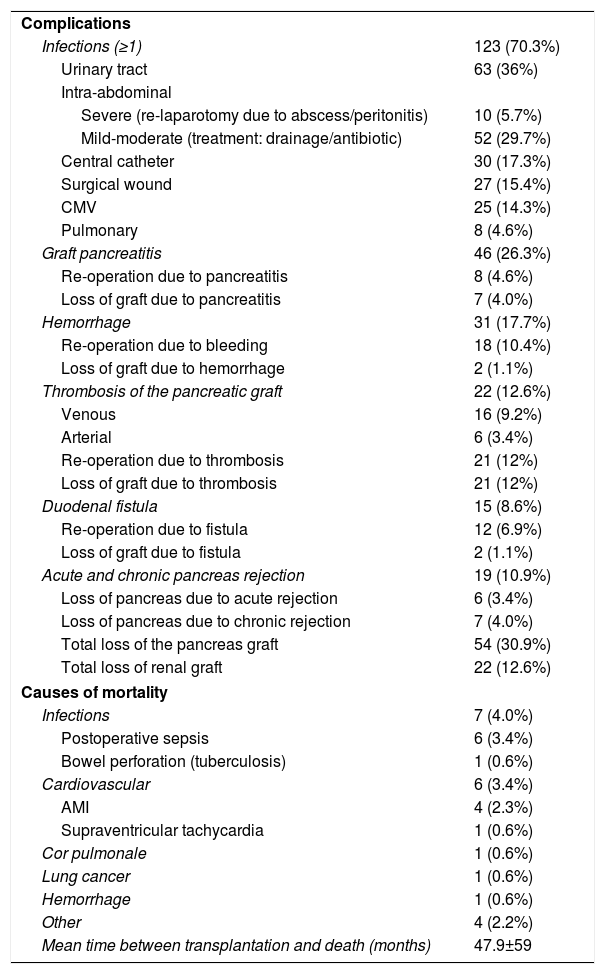
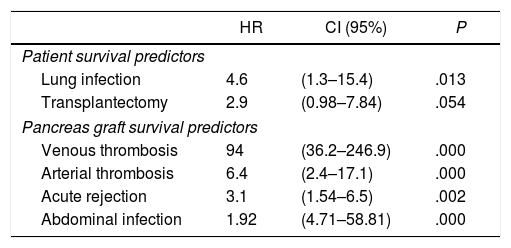
ResultsMedian age of the donors was 28years and mean age of recipients was 38.8±7.3years, being 103 males and 72 females. Enteric drainage of the exocrine pancreas was performed in 113 patients and bladder drainage in 62. Regarding post-transplant complications, the overall rate of infections was 70.3%; graft pancreatitis 26.3%; intraabdominal bleeding 17.7%; graft thrombosis 12.6%; and overall pancreas graft rejection 10.9%. The causes of mortality were mainly cardiovascular and infectious complications. Patient survival at 1, 3 and 5-year were 95.4%, 93% and 92.4%, respectively, and pancreas graft survival at 1, 3 and 5-year were 81.6%, 77.9% and 72.3%, respectively.
ConclusionsIn our 20-year experience of simultaneous pancreas–kidney transplantation, the morbidity rate, and 5-year patient and pancreas graft survivals were similar to those previously reported from the international pancreas transplant registries.
El trasplante de páncreas-riñón simultáneo constituye el tratamiento de elección en la diabetes tipo 1 o tipo 2 con fallo renal terminal o preterminal (diálisis o prediálisis), por ser la única terapia que consigue el estado euglucémico (insulino-independiente) en el paciente diabético.
MétodosEstudio retrospectivo y descriptivo de una serie de 175 pacientes trasplantados de páncreas-riñón simultáneo entre marzo de 1995 y abril de 2016. Se analizan las características de los donantes y receptores, variables perioperatorias e inmunosupresión, morbimortalidad postrasplante, supervivencia del paciente e injerto y factores de riesgo de supervivencia del paciente e injerto.
ResultadosLa mediana de edad de los donantes fue de 28 años y la media de los receptores, de 38,8±7,3años, siendo 103 hombres y 72 mujeres. La derivación duodeno-entérica se realizó en 113 casos y la duodeno-vesical, en 62. Las tasas de complicaciones postrasplante fueron las siguientes: infección global (70,3%), pancreatitis del injerto (26,3%), hemorragia intraabdominal (17,7%), trombosis del injerto (12,6%) y rechazo pancreático global (10,9%). Las causas de mortalidad fueron fundamentalmente cardiovasculares e infecciosas. La supervivencia del paciente a 1, 3 y 5años fue del 95,4, del 93 y del 92,4%, respectivamente, mientras que la del injerto correspondió al 81,6, al 77,9 y al 72,3%, respectivamente, durante el mismo periodo.
ConclusionesEn nuestra experiencia de 20 años de trasplante pancreático-renal simultáneo las tasas de morbilidad y supervivencia del paciente y del injerto a 5 años son similares a las referidas en los registros internacionales de trasplante pancreático.