The role that self-expanding stents play in the treatment of dehiscence after transthoracic esophagectomy is not well defined and controversial. Our aim is to describe the experience in a tertiary care hospital using these devices for treating dehiscence after Ivor Lewis esophagectomy.
MethodsDescriptive observational study of patients who suffered anastomotic dehiscence after a transthoracic esophagectomy, and especially those treated with stents, in the period between 2011 and 2016 at our hospital.
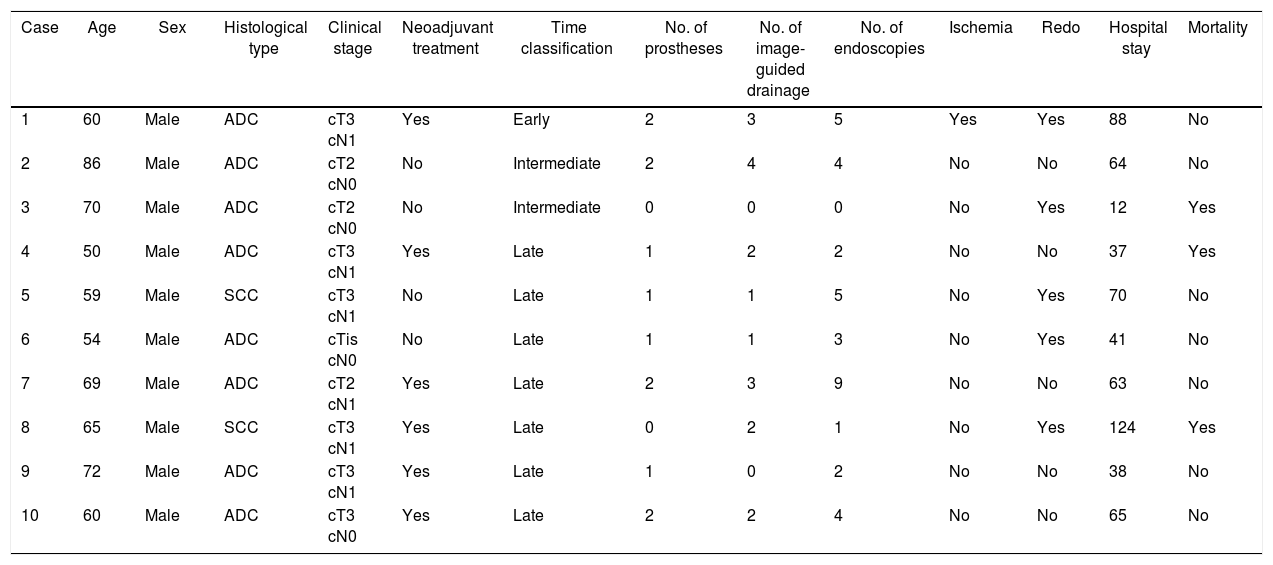
ResultsTen patients (11.8%) presented anastomotic dehiscence. Eight patients received stents, one of them died due to causes unrelated to the device. Stent migration was observed in one case, and the devices were maintained an average of 47.3 days. The stent was not effective only in one patient who suffered early dehiscence due to acute ischemia of the stomach. The two patients who did not receive stents died after reoperation.
ConclusionsStents are safe and effective devices that did not associate mortality in our series. They are especially indicated in intermediate or late-onset dehiscence and in fragile patients. The use of stents, together with mediastinal and pleural drainage, avoid reoperations with morbidity and mortality. Therefore, stents should be part of the usual therapeutic arsenal for the resolution of most suture dehiscences after Ivor Lewis esophagectomy. Randomized prospective studies would help to more precisely determine the role played by these devices in the treatment of dehiscence after transthoracic esophagectomy.
El papel que desempeñan las endoprótesis autoexpandibles en el tratamiento de las dehiscencias tras la esofagectomía transtorácica no está bien definido y resulta controvertido. Nuestro objetivo es mostrar la experiencia en un hospital de tercer nivel con el empleo de estos dispositivos en las dehiscencias tras la esofagectomía de Ivor Lewis.
MétodosEstudio observacional descriptivo de los pacientes que han presentado una dehiscencia de anastomosis tras una esofagectomía transtorácica y, en especial, de aquellos tratados mediante endoprótesis, en el periodo comprendido entre 2011 y 2016 en nuestro centro hospitalario.
ResultadosDiez pacientes (11,8%) presentaron una dehiscencia anastomótica, 8 de los cuales recibieron endoprótesis. Un paciente portador de endoprótesis falleció por causas ajenas a la misma. En un paciente se objetivó migración del dispositivo, manteniéndose una media de permanencia de 47,3 días. La prótesis no fue efectiva en un paciente que tuvo una dehiscencia precoz por isquemia aguda gástrica. Fallecieron los 2 pacientes que no recibieron endoprótesis después de la reintervención.
ConclusionesLas endoprótesis son dispositivos seguros y efectivos que no asocian mortalidad en nuestra serie. Están especialmente indicadas en dehiscencias intermedias o tardías y en pacientes frágiles, pues, junto con el drenaje mediastínico y pleural, evitan reintervenciones gravadas con morbimortalidad. Por tanto, las endoprótesis deben formar parte del arsenal terapéutico habitual para la resolución de la mayoría de las dehiscencias de sutura tras la esofagectomía de Ivor Lewis. La puesta en marcha de estudios prospectivos aleatorizados ayudaría a determinar con mayor precisión el papel que desempeñan estos dispositivos en el tratamiento de las dehiscencias tras una esofagectomía transtorácica.