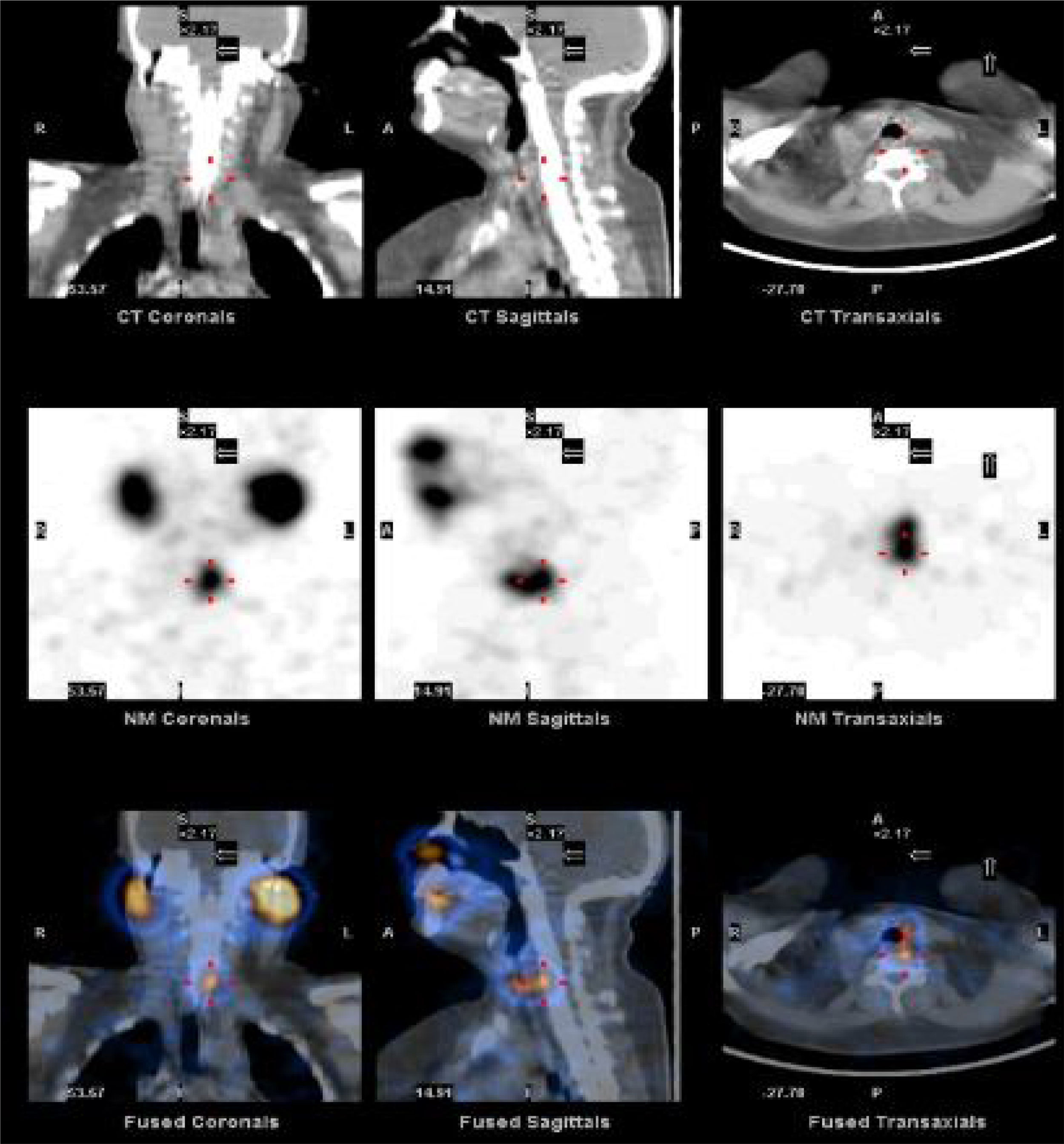
The BRAF V600E mutation in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) has been associated with resistance to 131I. Our aim was to quantify the response to 131I after surgery in patients who had the mutation (BRAF+) and those who did not have the mutated gene (BRAF−).
MethodA prospective cohort study was designed, from September 2015 to February 2016, which included patients with PTC receiving therapy after surgical treatment. Variables were described for age, gender, histology, tumor stage, thyroglobulin values before, 48h after and 6 months after 131I; absorbed dose and % activity on days 2 and 7 and elimination time.
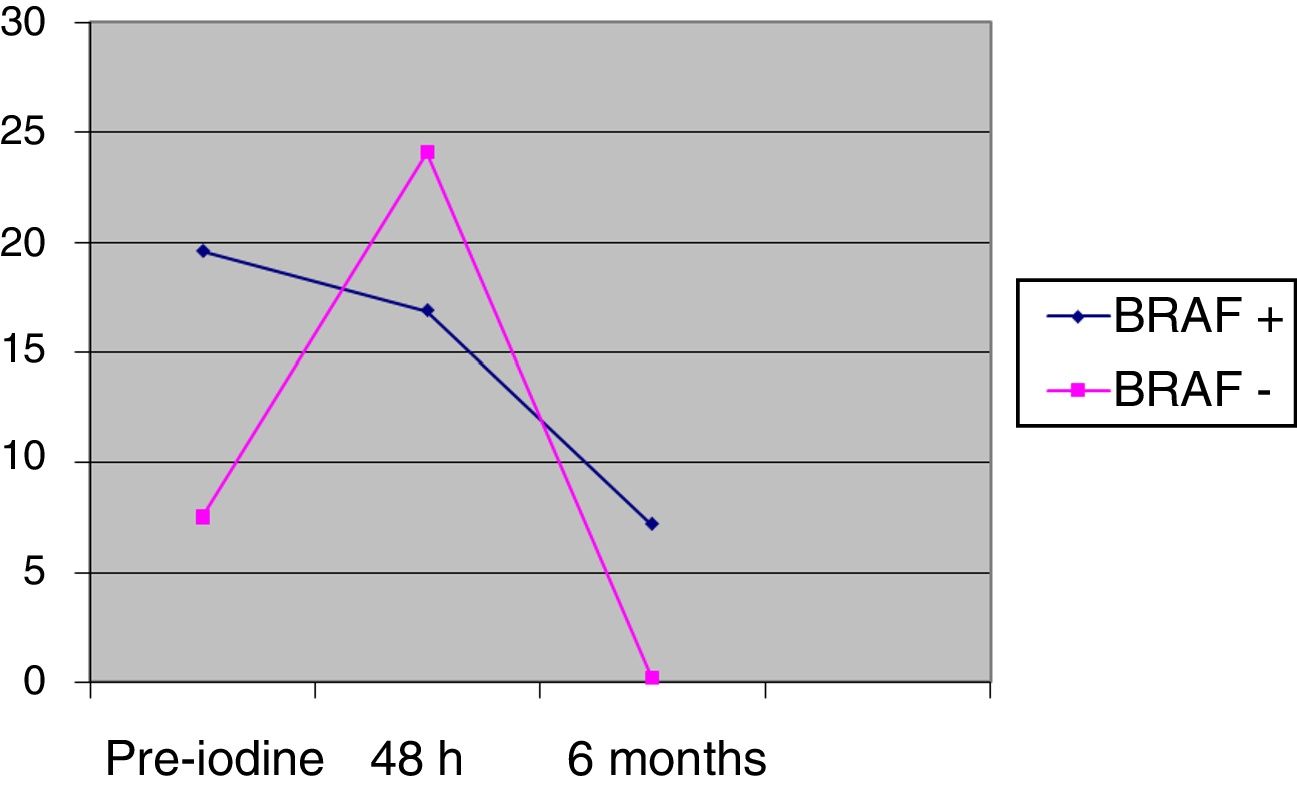
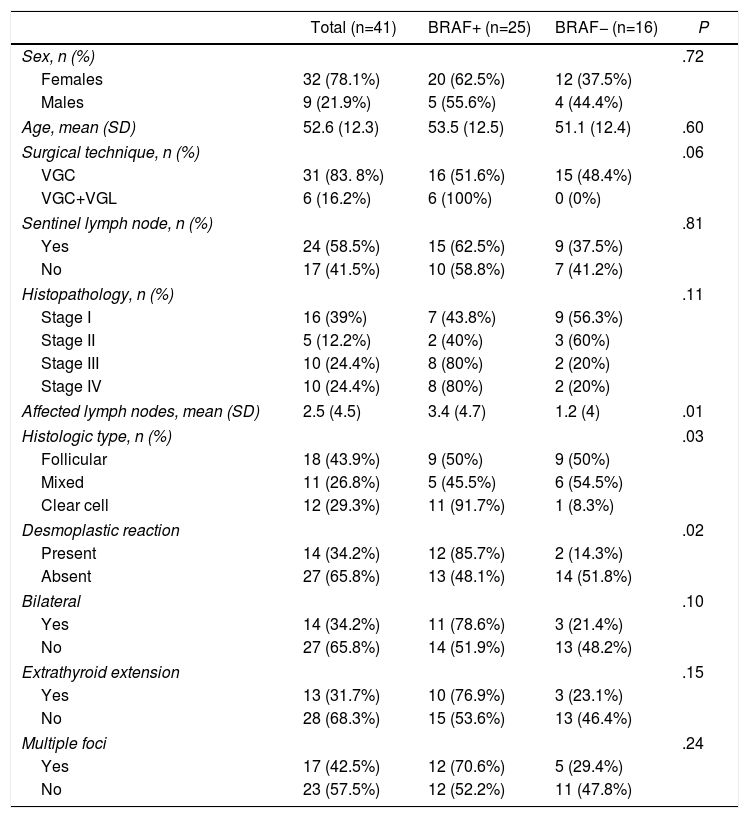
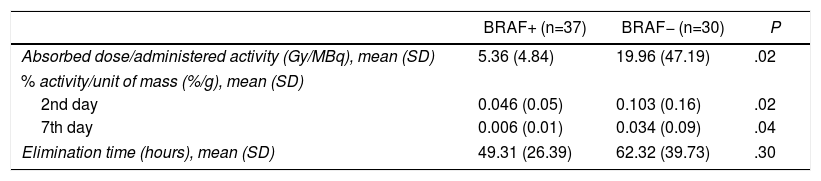
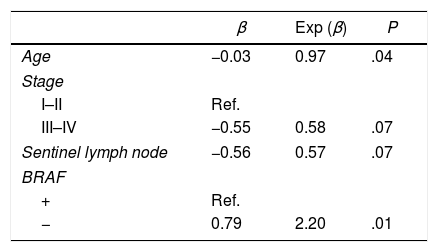
Results41 patients giving in total 67 thyroid remnants were included. 61% were BRAF+. In stages III and IV, 80% were BRAF+. In lateral resection, 100% were BRAF+. The number of nodes was higher in BRAF+: 3.4 vs 1.2 (P=.01). The classic variant was predominant in BRAF+ (91.7% vs 8.3%, P=.03). 85.7% vs 14.3% of BRAF+ had desmoplastic reaction (P=.02). The BRAF+ had a lower absorbed dose than the administered activity (5.4Gy/MBq vs 20Gy/MBq, P=.02); lower% activity with respect to the unit of mass at 2 (0.046%/g vs 0.103%/g, P=.02) and at 7 days (0.006%/gr vs 0.034%/gr, P=.04).
ConclusionsThe mutation of the BRAF V600E gene is related with greater resistance to postoperative treatment with 131I since the onset of the disease.
La mutación BRAF V600E en el cáncer papilar de tiroides (CPT) parece asociarse a una resistencia al 131I. Nuestro principal objetivo fue cuantificar la respuesta al 131I tras la cirugía tanto en pacientes que presentaban la mutación (BRAF+) como en los que no presentaban el gen mutado (BRAF−).
MétodoEstudio prospectivo de los CPT intervenidos y tratados con 131I desde septiembre de 2015 hasta enero de 2017. Variables: edad, género, estadio tumoral, histológicas, tiroglobulina antes de 131I, a las 48h y a los 6meses; dosis absorbida y % de actividad a los 2 y a los 7días y tiempo de eliminación.
ResultadosCuarenta y un pacientes y 67 restos tiroideos. El 61% eran BRAF+. En los estadios III y IV, el 80% eran BRAF+. En el vaciamiento ganglionar terapéutico, el 100% eran BRAF+. El número de ganglios fue superior en BRAF+: 3,4 vs 1,2 (p=0,01). La variante clásica fue predominante en BRAF+ (91,7% vs 8,3%; p=0,03). El 85,7% vs 14,3% de los BRAF+ tuvieron reacción desmoplásica (p=0,02). Los BRAF+ presentaban menor dosis absorbida respecto a la actividad administrada (5,4 vs 20Gy/MBq; p=0,02); menor % de actividad respecto a la unidad de masa a los 2 (0,046 vs 0,103%/g; p=0,02) y a los 7días (0,006 vs 0,034%/g, p=0,04).
ConclusionesLa mutación del gen BRAF V600E se relaciona con una mayor resistencia al tratamiento posquirúrgico con 131I desde el inicio de la enfermedad.