The marked decrease in LDL-C levels produced by the inhibitors of the plasma proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (iPCSK9) could be associated with an increased risk of cataracts.
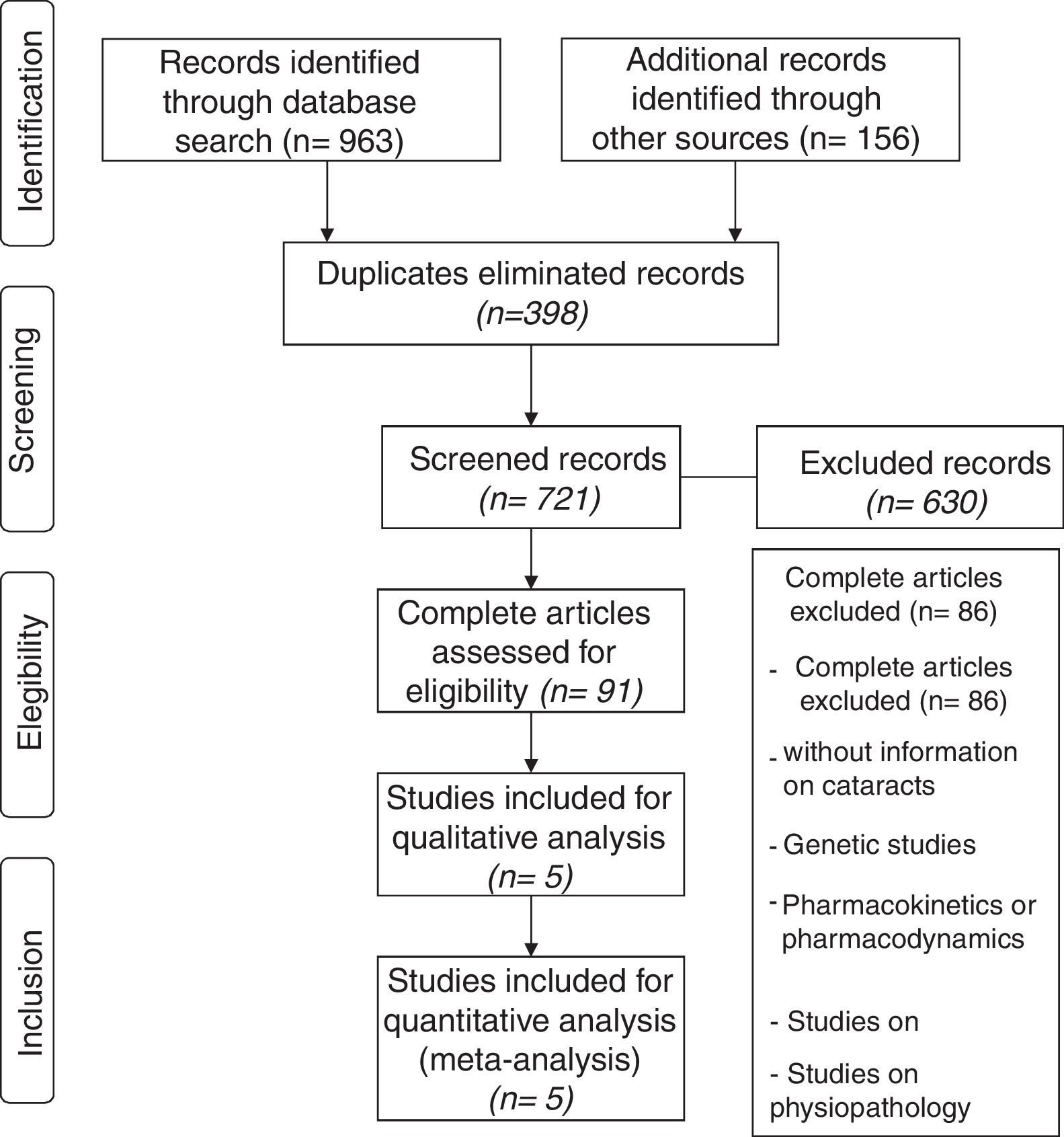
MethodsA meta-analysis was performed that included randomized clinical trials controlled with iPCSK9, alone, or in combination with other lipid-lowering drugs, which reported new cases of cataracts, by searching PubMed/Medline, databases of EMBASE and Cochrane Clinical Trials. A fixed-effect model was used, and a meta-regression was carried out evaluating the relationship between intra-treatment LDL-C and the risk of developing cataracts.
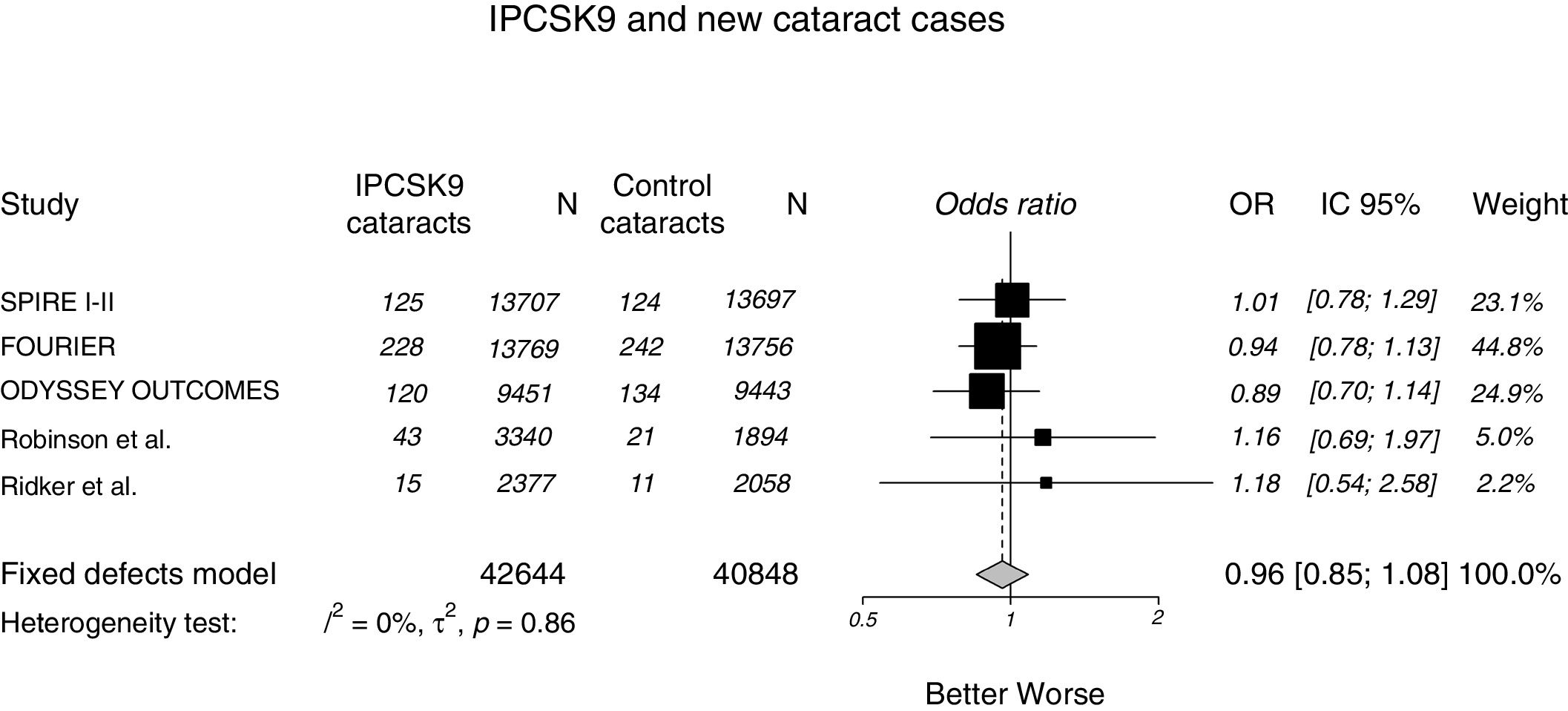
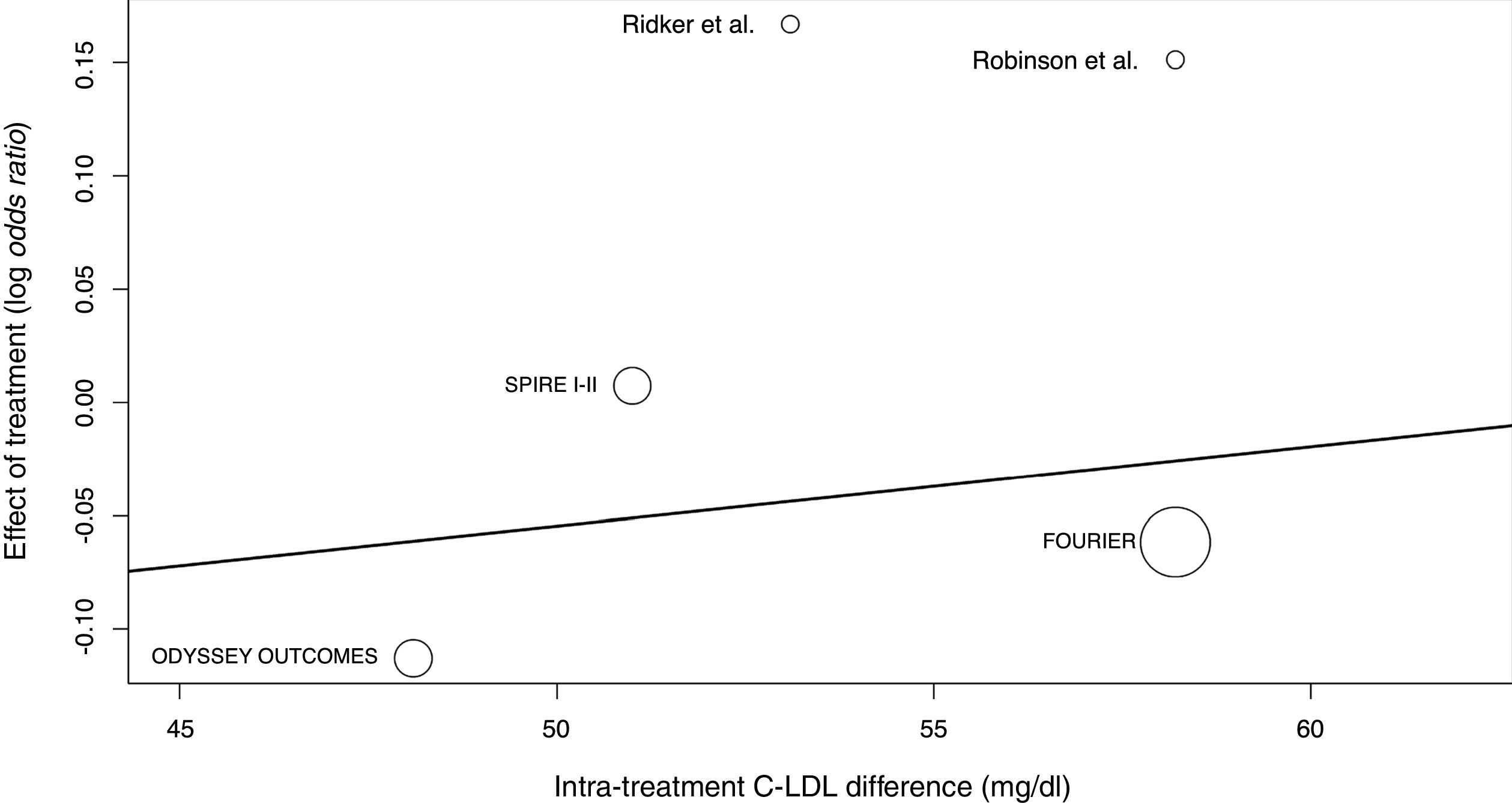
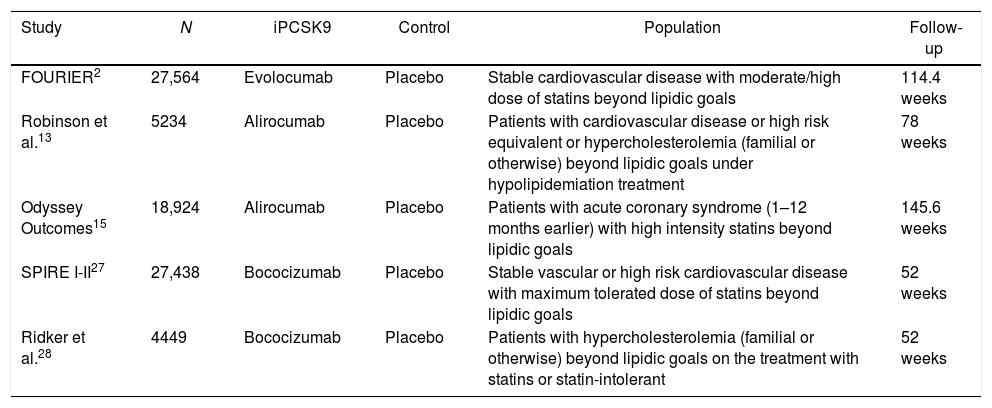
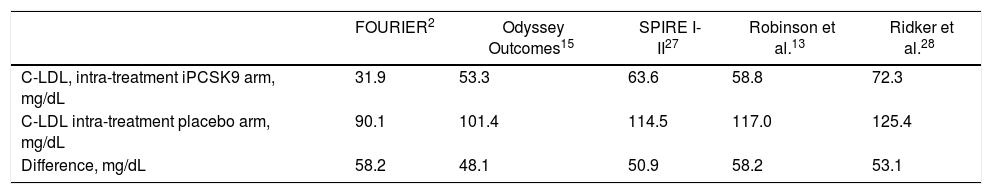
ResultsFive eligible studies of iPCSK9 including 83,492 patients were taken into account for the analysis, and 531 new cases of cataracts in iPCSK9 group vs. 532 in placebo group were diagnosed. The iPCSK9 therapy was not associated with an increased risk of cataracts [OR: 0.96, 95% CI: 0.85–1.08; p=0.86, I2: 0%]. Likewise, no significant association was found between on-treatment LDL-C levels, differences between study arms, and new cases of cataracts.
ConclusionIn this analysis, the use of iPCSK9 was not associated with an increased risk of cataracts.
El marcado descenso en los niveles de C-LDL producidos por los inhibidores de la proproteína convertasa plasmática subtilisina kexina tipo 9 (iPCSK9) podría asociarse con un mayor riesgo de cataratas.
MétodosRealizamos un metaanálisis que incluyó ensayos clínicos aleatorizados y controlados con iPCSK9, solos o combinados con otros fármacos hipolipidemiantes, que reportaron nuevos casos de cataratas, buscando en PubMed/Medline, bases de datos de EMBASE y Cochrane Clinical Trials. Se utilizó un modelo de efectos fijos y se realizó una metarregresión evaluando la relación entre el C-LDL intratratamiento y el riesgo de desarrollar cataratas.
ResultadosSe tomaron en cuenta 5 estudios elegibles con iPCSK9 que incluyeron 83.492 pacientes para el análisis, refiriendo 531 nuevos casos de cataratas en el grupo con iPCSK9 frente a 532 en el grupo placebo. La terapia con iPCSK9 no se asoció con un mayor riesgo de presentar cataratas (OR: 0,96; IC 95%: 0,85–1,08; p=0,86, I2: 0%]. Asimismo, no se encontró una asociación significativa entre la diferencia de C-LDL intratratamiento entre las ramas de los estudios y el riesgo de cataratas.
ConclusiónEn nuestro análisis, la utilización de iPCSK9 no se asoció con un mayor riesgo de cataratas.