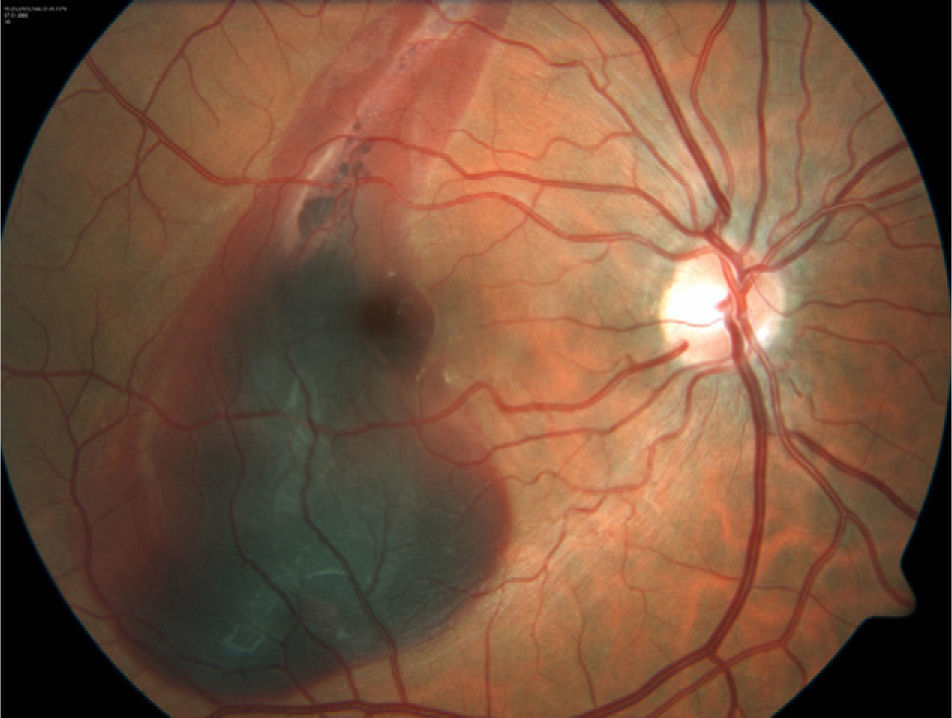
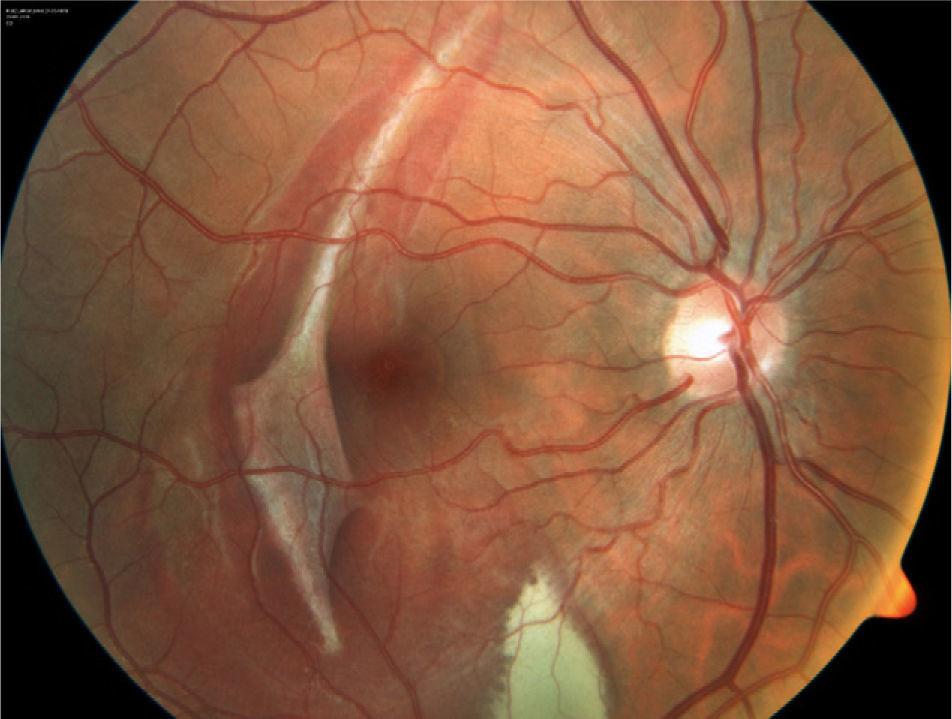
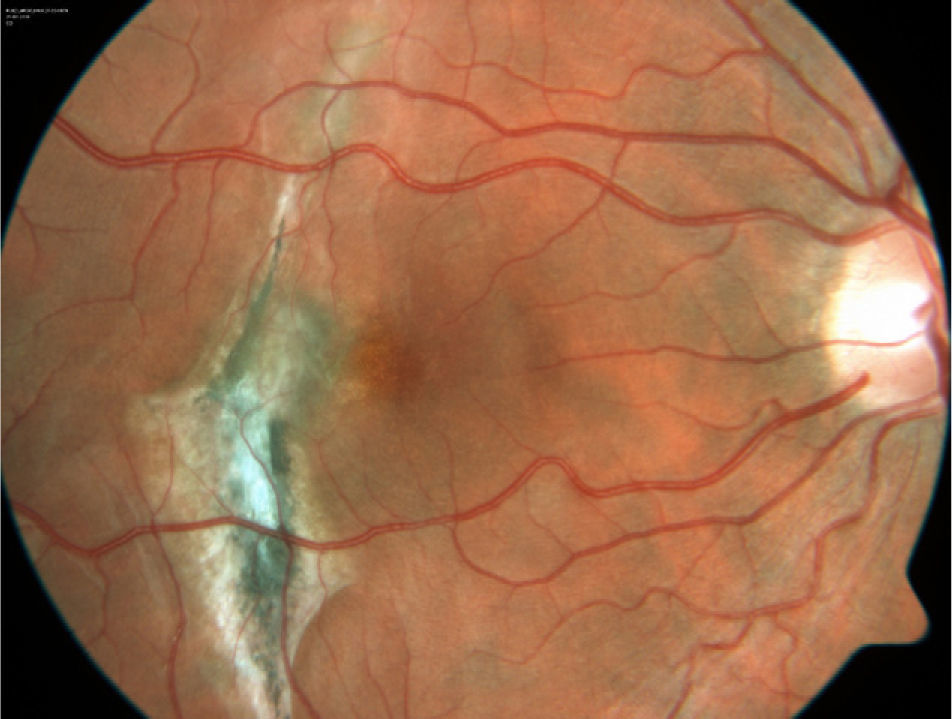
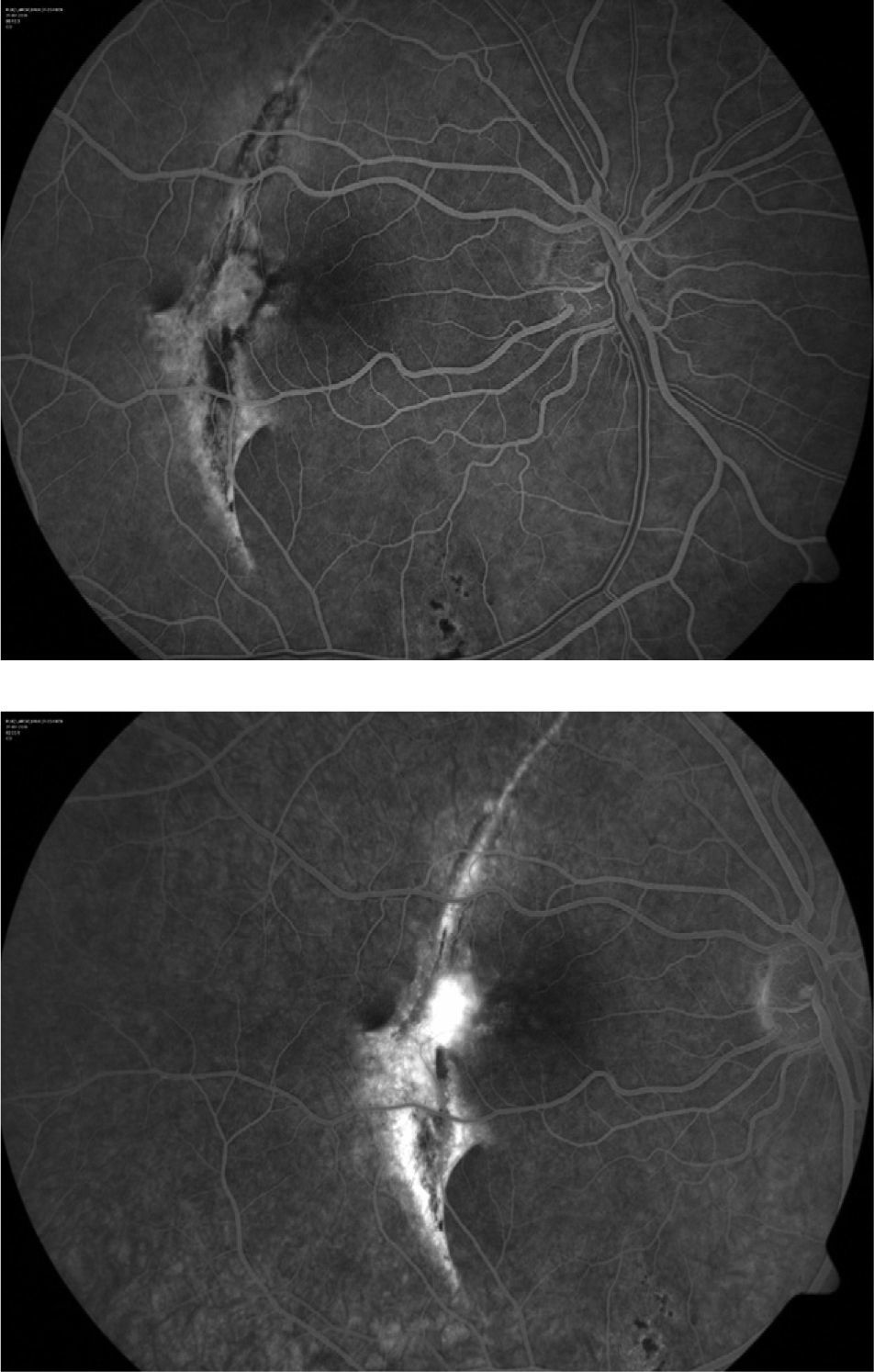
A 28-year-old male attended our Emergency Department with a traumatic choroidal rupture and macular haemorrhage. After pneumatic displacement of the haemorrhage with C3F8 and tissue plasminogen activator, the haemorrhage was reabsorbed and visual acuity (VA) improved. Three months later the patient presented with decreased VA and a juxtafoveal choroidal neovascularization (CNV) that was treated with intravitreal bevacizumab. One year after a single bevacizumab injection the CNV remained inactive, with a final VA of 0.5.
DiscussionIntravitreal bevacizumab injection is a new and effective treatment for traumatic CNV. In our patient, in contrast to other aetiologies, the CNV needed no more than one Avastin® injection to be inactivated, after one year of follow-up.
Paciente varón de 28 años que presenta rotura coroidea y hemorragia macular postraumáticas de 24 horas de evolución acude al servicio de urgencias. Se realizó desplazamiento neumático de la hemorragia mediante inyección intravítrea de C3F8 y activador tisular del plasminógeno (rTPA), consiguiéndose la reabsorción de la hemorragia y mejora de la agudeza visual (AV). Al cabo de 3 meses, el paciente acude por empeoramiento de la visión con metamorfopsia, diagnosticándose de neovascularización (NVC) yuxtafoveal en la zona de la rotura, que se trata con una inyección de bevacizumab intravítreo. Un año después, la NVC permanece inactiva y la AV se mantiene en 0,5.
DiscusiónLa inyección intravítrea de bevacizumab representa una nueva forma efectiva de tratamiento de la NVC postraumática. A diferencia de lo descrito en otras etiologías, la NVC secundaria a rotura coroidea en nuestro paciente requirió solamente una dosis de Avastin® para su inactivación, en un periodo de seguimiento de un año.