To evaluate complications, morbidity and oncologic outcomes of pelvic exenteration as treatment for gynecologic malignancies.
Materials and methodsBetween 2008 and 2015, a total of 35 patients underwent pelvic exenteration, due to recurrence of gynecological cancer. Surgical outcomes, early and late postoperative complications, and recurrence/survival outcomes were assessed.
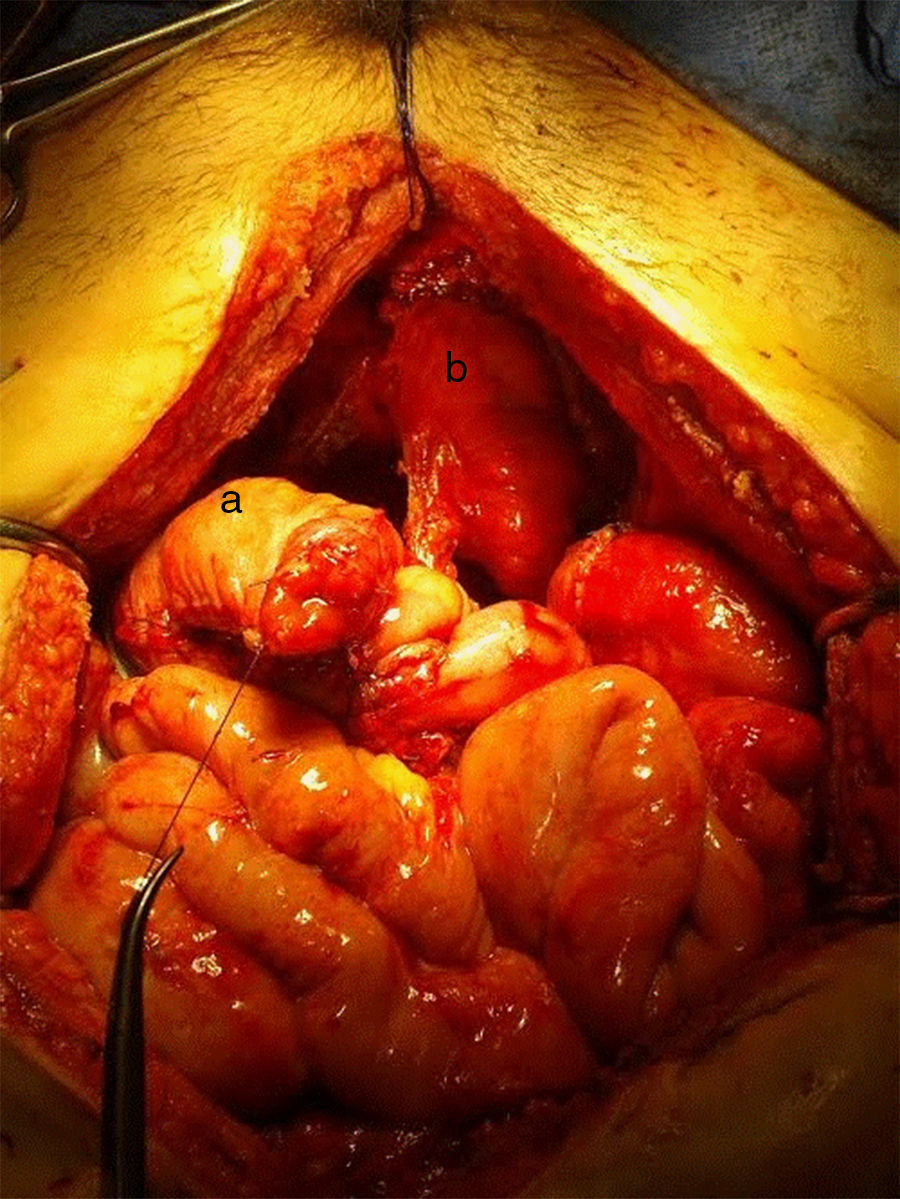
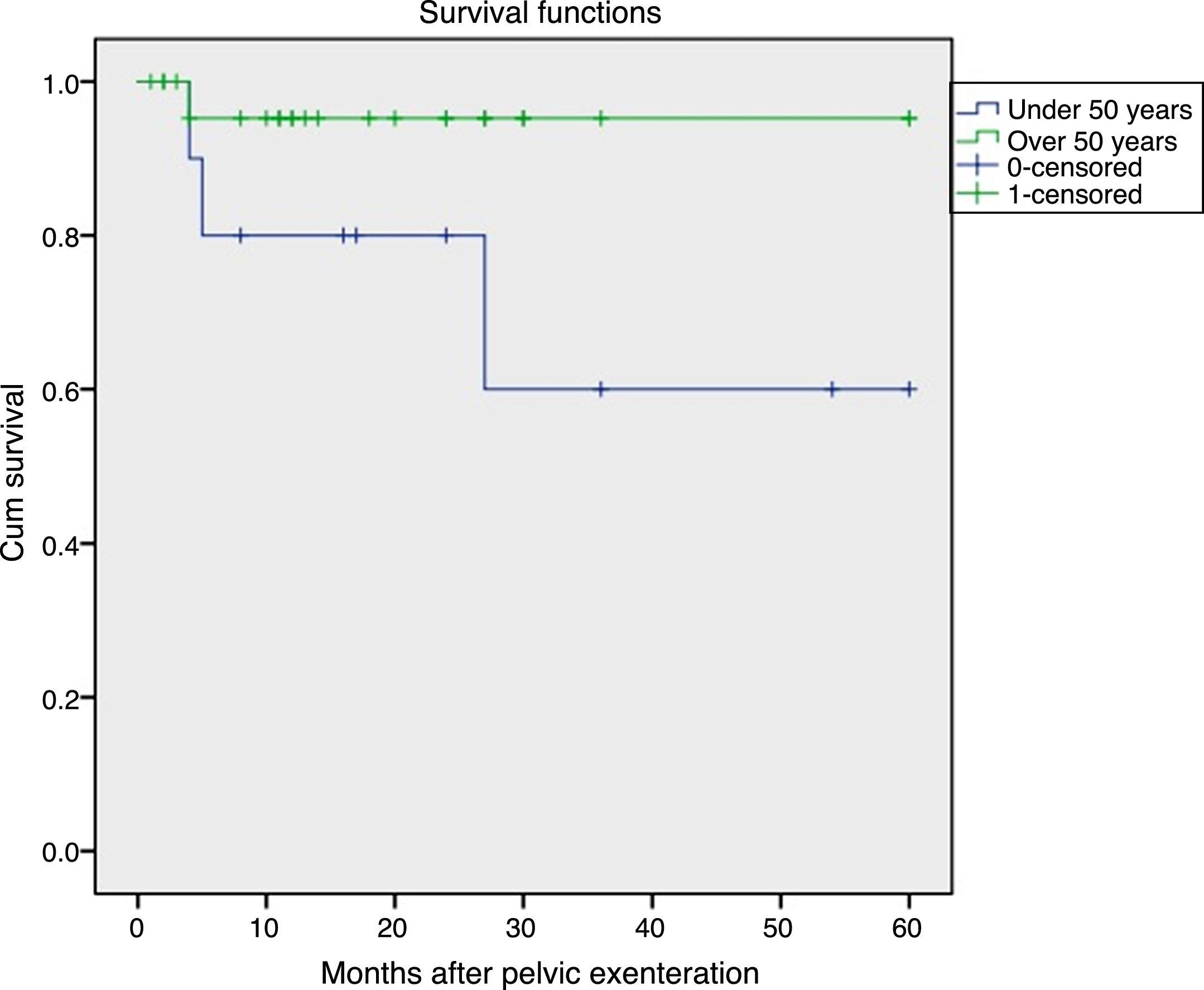
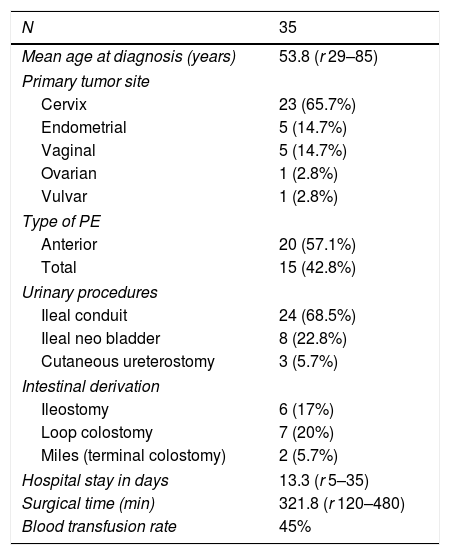
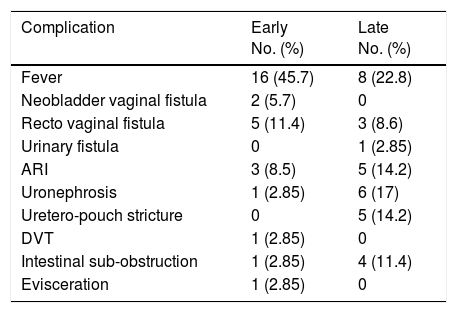
ResultsMean patient age was 53.8 years. Anterior exenteration was done in 20 patients, while 15 were total exenterations. Ileal conduit was done in 24 patients, while 8 received a neobladder and 3 a cutaneous ureterostomy. Postoperative complications were divided in 2 groups, early (<30 days) and late complications (>30 days). A total of 25 patients (71.4%) had one or more early complications; 16 (45.7%) had fever due to a urinary tract infection, pyelonephritis or intra-abdominal collection; 2 (5.7%) developed a vesicovaginal fistula; 4 (11.4%) a rectovaginal fistula; 3 (8.5%) acute kidney failure and one (2.85%) uronephrosis. Regarding to late complications, 8 patients (22.8%) had fever. Six (17%) presented with uronephrosis, and 5 (14.2%) with ureteral-pouch stricture. Five patients (14.2%) had acute renal insufficiency, 3 (8,6%) rectovaginal fistula and one (2.85%) urinary fistula. Mean follow up time was 20.3 month (2–60). A total of 22 patients (62.8%) were free of disease. Another 13 (37.1%) patients relapsed. Only 4 (11.4%) patients died after pelvic exenteration due to underlying disease.
ConclusionPelvic exenteration has a high rate of complications and morbidity, but can be the last curative opportunity in patients with recurrent or persistent gynecologic malignancies.
This procedure should be performed by multidisciplinary, experienced teams in a tertiary medical center.
Evaluar las complicaciones, morbilidad y resultados oncológicos de la exenteración pelviana como tratamiento para los tumores ginecológicos.
Materiales y métodosEntre enero de 2008 y diciembre de 2015, 35 pacientes fueron tratadas mediante exenteración pelviana debido a recurrencia de cáncer de origen ginecológico. Se evaluaron resultados quirúrgicos, complicaciones postoperatorias tempranas y tardías, recurrencia y sobrevida.
ResultadosLa edad media de las pacientes fue de 53,8 años. Se realizó exenteración anterior en 20 pacientes, mientras que en 15 se realizó exenteración total. En 24 pacientes se realizó derivación urinaria de tipo Bricker, neovejiga ileal en 8 y ureterostomía cutánea en 3.
Las complicaciones postoperatorias se dividieron en 2 grupos: tempranas (<30 días) y tardías (>30 días).
Un total de 25 pacientes (71,4%) tuvieron una o más complicaciones tempranas; 16 (45,7%) tuvieron fiebre debido a infección urinaria, pielonefritis o colección intraabdominal; 2 (5,7%) evolucionaron con fístula vesicovaginal; 4 (11,4%) con fístula recto vaginal; 3 (8,5%) con insuficiencia renal aguda y uno (2,85%) con uronefrosis. Con respecto a las complicaciones tardías, 8 pacientes (22,8%) tuvieron fiebre. Seis (17%) se presentaron con uronefrosis y 5 (14,2%) con estenosis uretero-pouch. Cinco pacientes (14,2%) tuvieron insuficiencia renal aguda, 3 (8,6%) fístula recto vaginal y una (2,85%) fístula urinaria. El tiempo de seguimiento medio fue de 20,3 meses (rango 2-60). En total, 22 pacientes (62,8%) permanecieron libres de enfermedad. Otras 13 pacientes (37%) recayeron y 4 pacientes (11,4%) murieron luego de la exenteración pelviana debido a la enfermedad de base. No hubo muertes relacionadas a la cirugía.
ConclusiónLa exenteración pelviana tiene una alta tasa de complicaciones, pero puede ser la última oportunidad curativa en pacientes con tumores ginecológicos.
Este procedimiento debería llevarse a cabo por equipos multidisciplinarios, con experiencia, en centros médicos de alta complejidad.