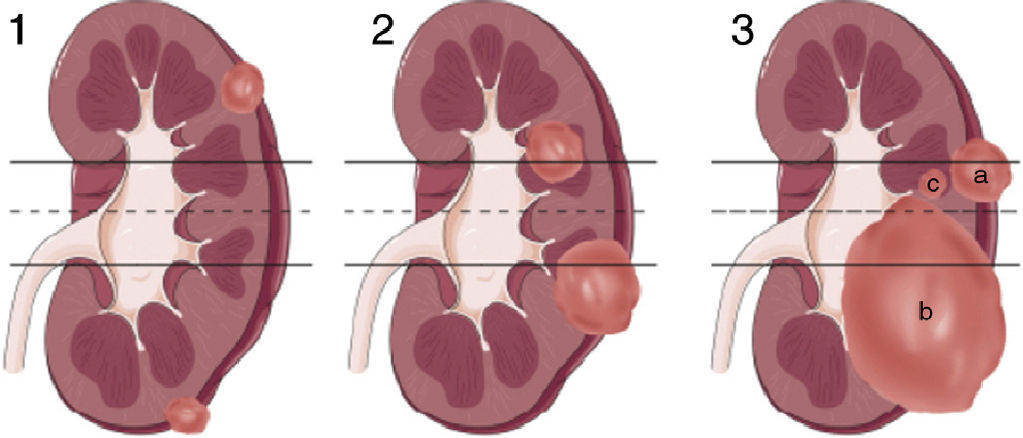
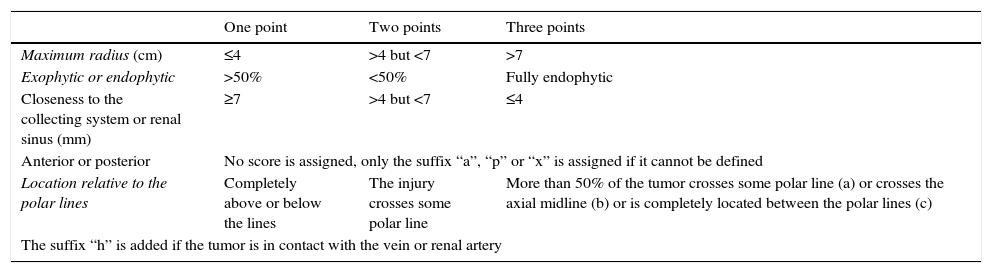
The growing incidence of renal masses and the wide range of available treatments require predictive tools that support the decision making process. The RENAL index – Radius; Exophytic/endophytic; Nearness to sinus; Anterior/posterior; Location relative to polar lines – helps standardize the anatomy of a renal mass by differentiating three groups of complexity. Since the introduction of the index, there have been a growing number of studies, some of which have been conflicting, that have evaluated the clinical utility of its implementation.
ObjectiveTo analyze the scientific evidence on the relationship between the RENAL index and the main strategies for managing renal masses.
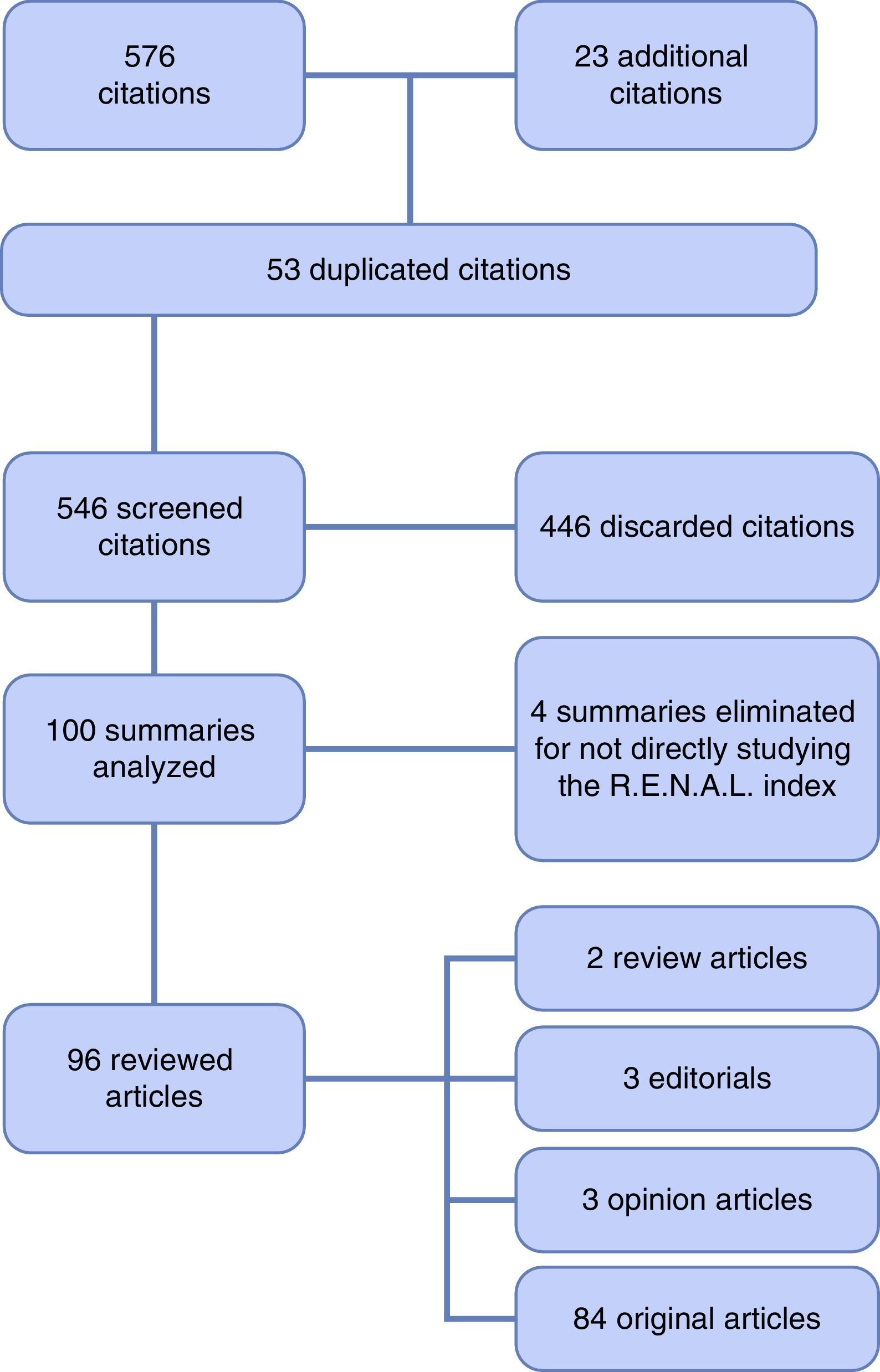
Acquisition of the evidenceA search was conducted in the Medline database, which found 576 references on the RENAL index. In keeping with the PRISM Declaration, we selected 100 abstracts and ultimately reviewed 96 articles.
Synthesis of the evidenceThe RENAL index has a high degree of interobserver correlation and has been validated as a predictive nomogram of histological results. In active surveillance, the index has been related to the tumor growth rate and probability of nephrectomy. In ablative therapy, the index has been associated with therapeutic efficacy, complications and tumor recurrence. In partial nephrectomy, the index has been related to the rate of complications, conversion to radical surgery, ischemia time, function preservation and tumor recurrence, a finding also observed in radical nephrectomy.
ConclusionsThe RENAL index is an objective, reproducible and useful system as a predictive tool of highly relevant clinical parameters such as the rate of complications, ischemia time, renal function and oncological results in the various currently accepted treatments for the management of renal masses.
La creciente incidencia de las masas renales y el amplio abanico de tratamientos disponibles hacen necesario el establecimiento de herramientas predictivas que apoyen la toma de decisiones. El índice RENAL – Radius; Exo/endophitic; Nearnes to sinus; Anterior/posterior; Location relative to polar lines – permite estandarizar la anatomía de una masa renal diferenciando 3 grupos de complejidad. Desde su presentación existe una creciente, y a veces contradictoria, literatura que evalúa la utilidad clínica de su aplicación.
ObjetivoAnalizar la evidencia científica sobre la relación entre el índice RENAL y las principales estrategias para el manejo de una masa renal.
Adquisición de la evidenciaSe realizó una búsqueda en la base de datos Medline, encontrando 576 citas bibliográficas sobre el índice RENAL. De acuerdo con la Declaración PRISMA se seleccionaron 100 resúmenes y finalmente se revisaron 96 artículos.
Síntesis de la evidenciaEl índice RENAL tiene un alto grado de concordancia interobservador y ha sido validado como nomograma predictivo de resultado histológico. En vigilancia activa se ha relacionado con la velocidad de crecimiento tumoral y la probabilidad de nefrectomía. En terapia ablativa se ha asociado con la eficacia terapéutica, complicaciones y recidiva tumoral. En nefrectomía parcial se ha relacionado con la tasa de complicaciones, la conversión a cirugía radical, el tiempo de isquemia, la preservación funcional y la recidiva tumoral, hallazgo también observado en nefrectomía radical.
ConclusionesEl índice RENAL es un sistema objetivo, reproducible y útil como herramienta predictiva de parámetros clínicos tan relevantes como la tasa de complicaciones, el tiempo de isquemia, la función renal y los resultados oncológicos en los diversos tratamientos actualmente aceptados para el manejo de una masa renal.