The revolution of digital technologies constitutes a new setting for the patient–physician relationship and provides patients with a scenario of privacy and universal access to a vast amount of information. However, there is little information on how digital resources are used and what their advantages and disadvantages are.
ObjectivesTo explore the scope of the scientific research on the use of digital technology related to men's sexual disorders and to analyze the primary sources of digital information related to this field.
Acquisition of evidenceSystematic searches of the scientific literature, websites (10 first results in each google search) and mobile applications (apps). The searches combined the keywords “web” and “app” with “erectile dysfunction”, “premature ejaculation”, “Peyronie”, “male hypogonadism”, and “infertility”. Websites and apps were assessed for quality according to predefined indicators.
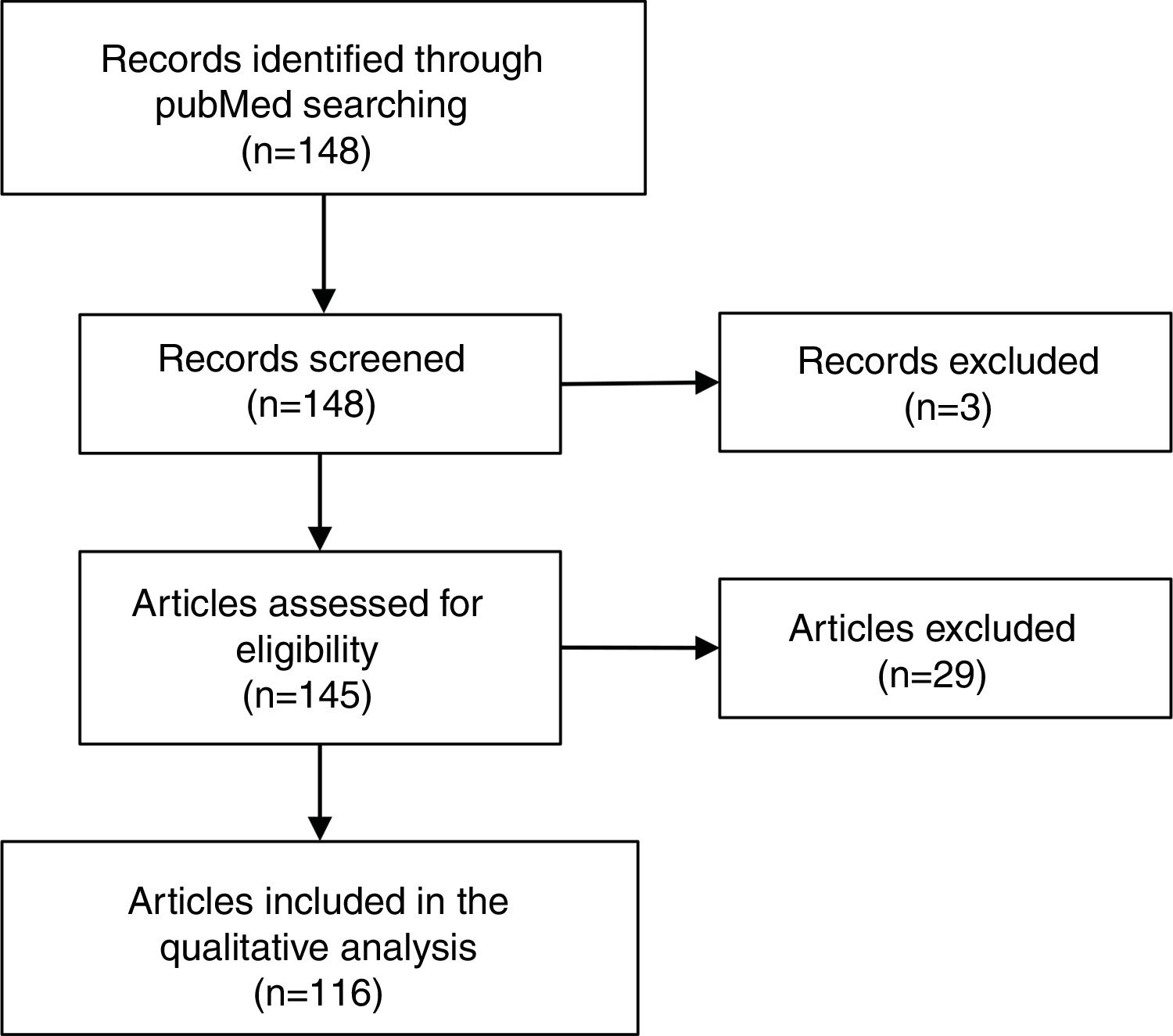
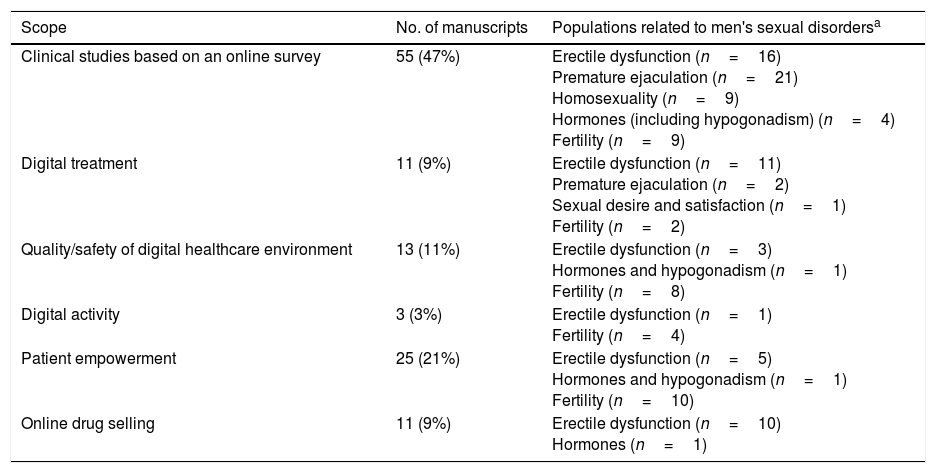
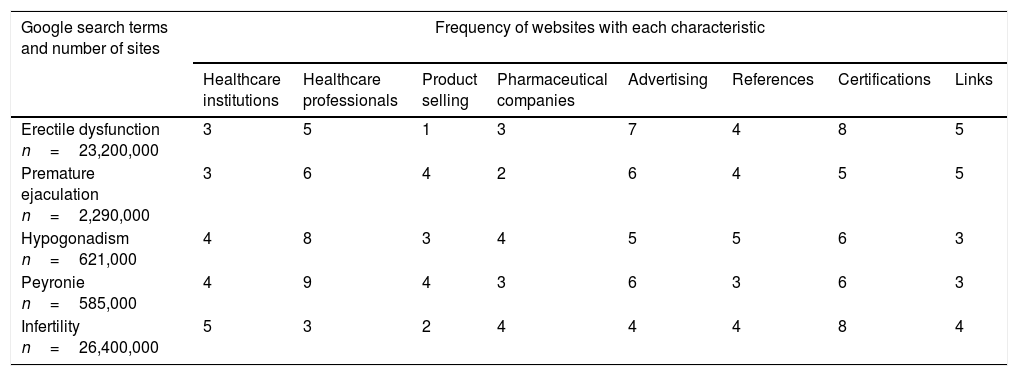
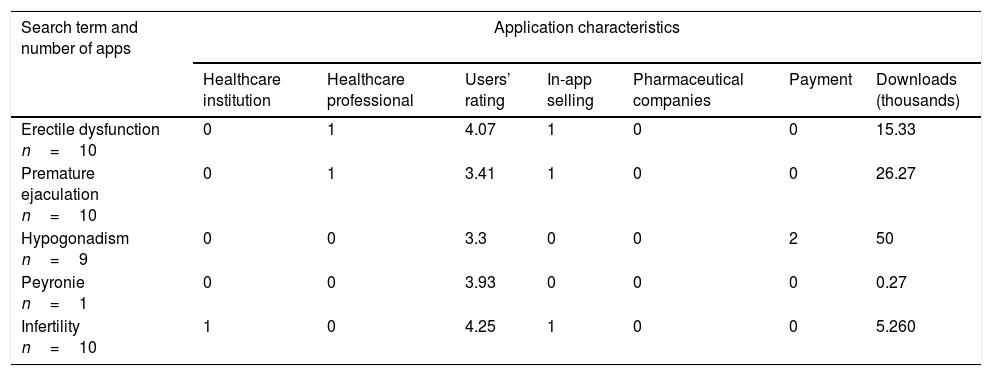
Synthesis of evidenceThe qualitative analysis of the scientific literature included 116 manuscripts; 47% were clinical studies based on online survey, 9% dealt with digital treatments, 11% with quality/safety of digital healthcare environment, 3% with digital activity, 21% with patient empowerment, and 9% with online drug selling. Of 50 websites assessed for quality, 29 (58%) scored 4 or 5 on a 5-point Likert scale. The app search yielded 40 apps; only 3 of them (8%) reported the identity of a health center or healthcare professional involved.
ConclusionsPatients and healthcare professionals may benefit from digital resources related to men's sexual disorders; however, a strong commitment by the scientific and healthcare community is essential to increase the quality of these resources.
La revolución de las tecnologías digitales constituye un nuevo escenario para las relaciones médico-paciente y proporciona a los pacientes un espacio de privacidad y acceso universal al conocimiento. Sin embargo, existe poca información acerca del uso de los recursos digitales, así como de sus ventajas e inconvenientes.
ObjetivosExplorar el ámbito de la investigación científica en cuanto al uso de recursos digitales relacionados con los trastornos sexuales masculinos y analizar las principales fuentes de información en estos campos.
Adquisición de la evidenciaBúsquedas sistemáticas en la literatura científica, páginas web (10 primeros resultados en cada búsqueda de google) y aplicaciones móviles (apps). Las búsquedas combinaron las palabras clave «web» y «app» con «erectile dysfunction», «premature ejaculation», «Peyronie», «male hypogonadism», y «infertility». La calidad de las páginas web y apps fue analizada según indicadores predefinidos.
Síntesis de la evidenciaEl análisis cualitativo de la literatura científica incluyó 116 artículos, el 47% de los cuales eran estudios basados en encuestas online, el 9% abordaban los tratamientos digitales, el 11% la calidad/seguridad del entorno digital en salud, el 3% la actividad digital, el 21% el empoderamiento de los pacientes y el 9% las ventas de fármacos online. De las 50 páginas web evaluadas, 29 (58%) puntuaron 4 o 5 en una escala Likert de 5 puntos. La búsqueda de apps resultó en 40 apps; únicamente 3 de ellas (8%) aportaban la identidad de algún centro de salud o profesional implicado.
ConclusionesTanto los pacientes como los profesionales sanitarios pueden beneficiarse de los recursos digitales relacionados con los trastornos sexuales masculinos. No obstante, es necesaria una mayor implicación de la comunidad médica para incrementar la calidad de dichos recursos.