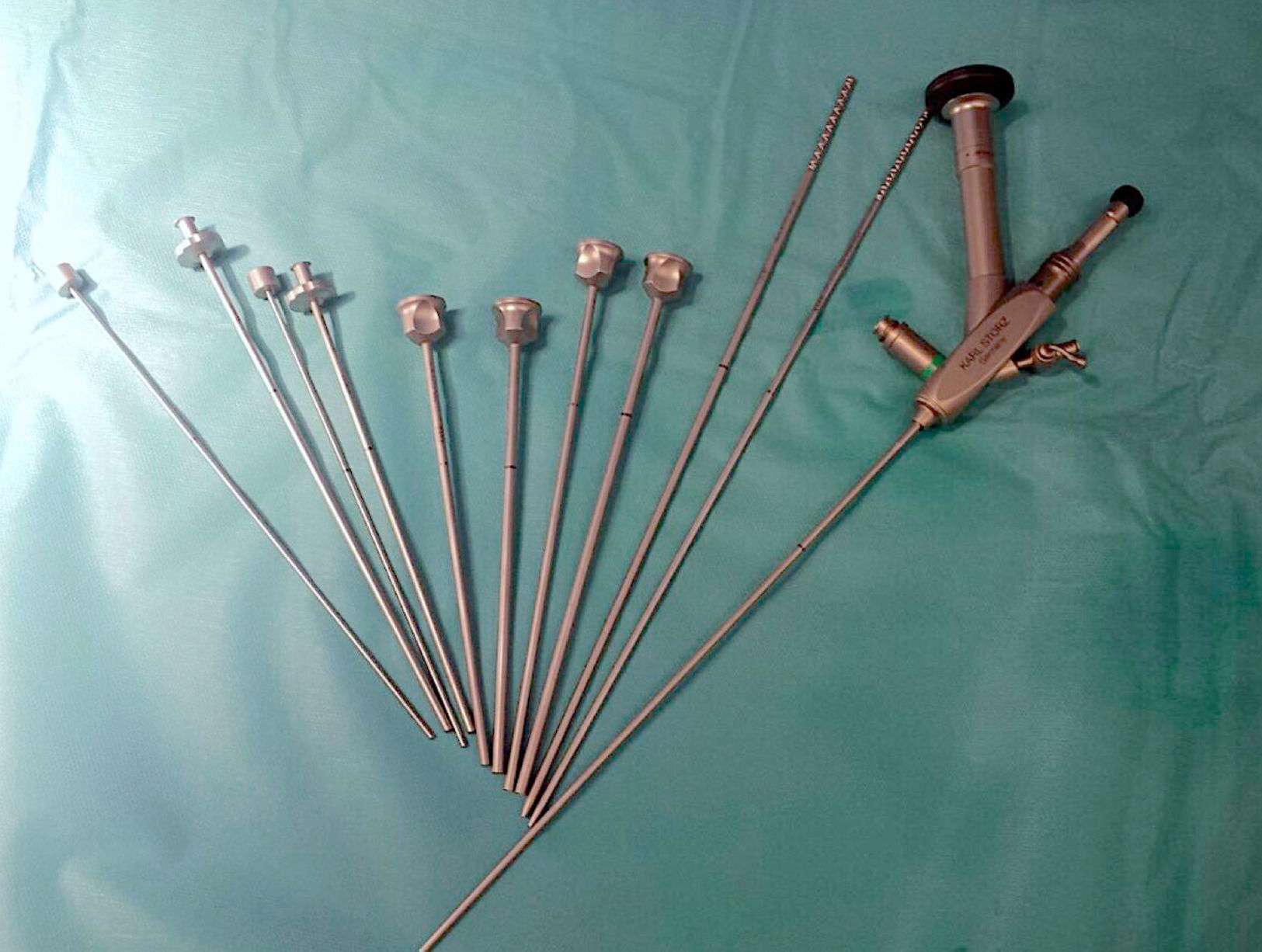
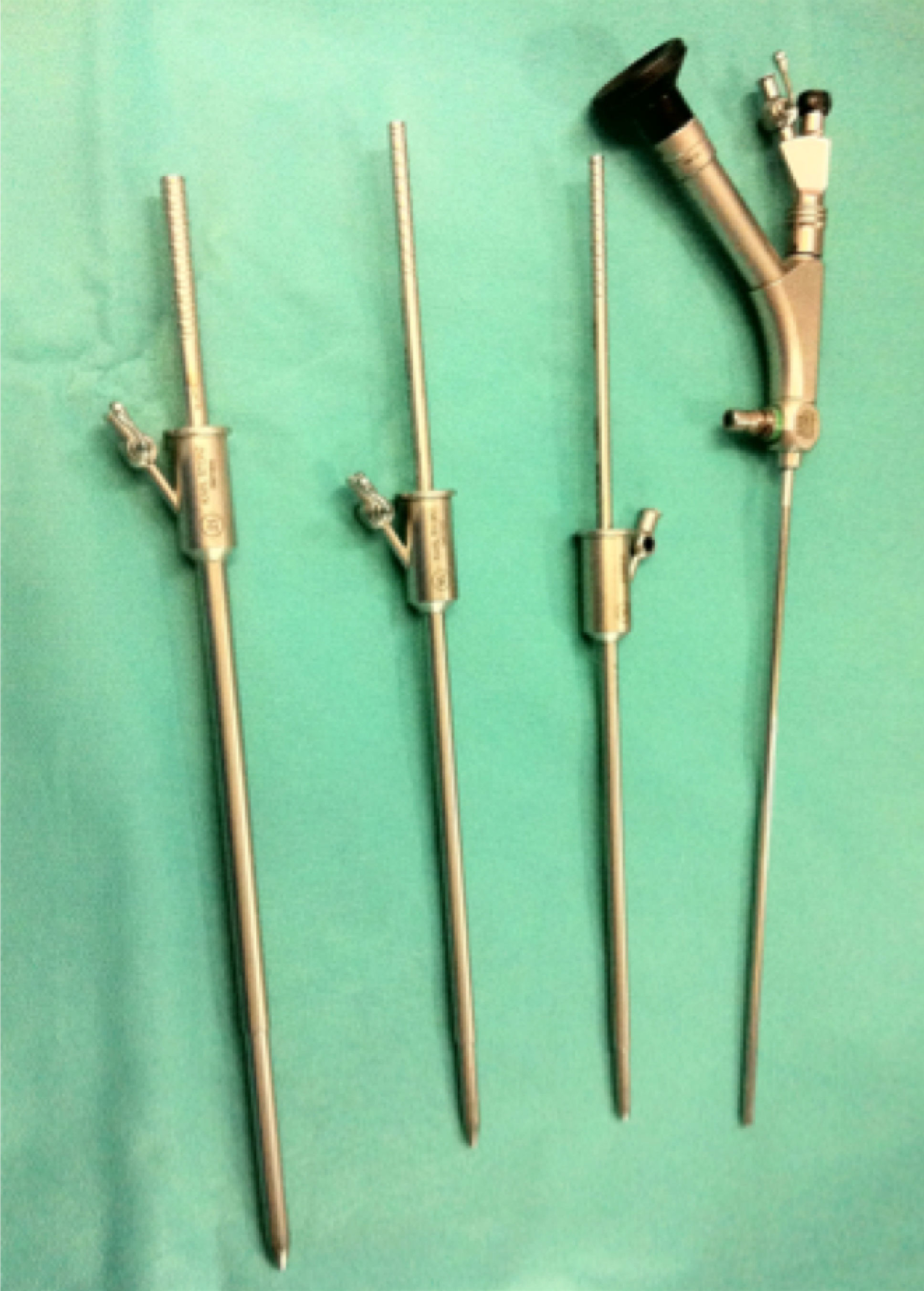
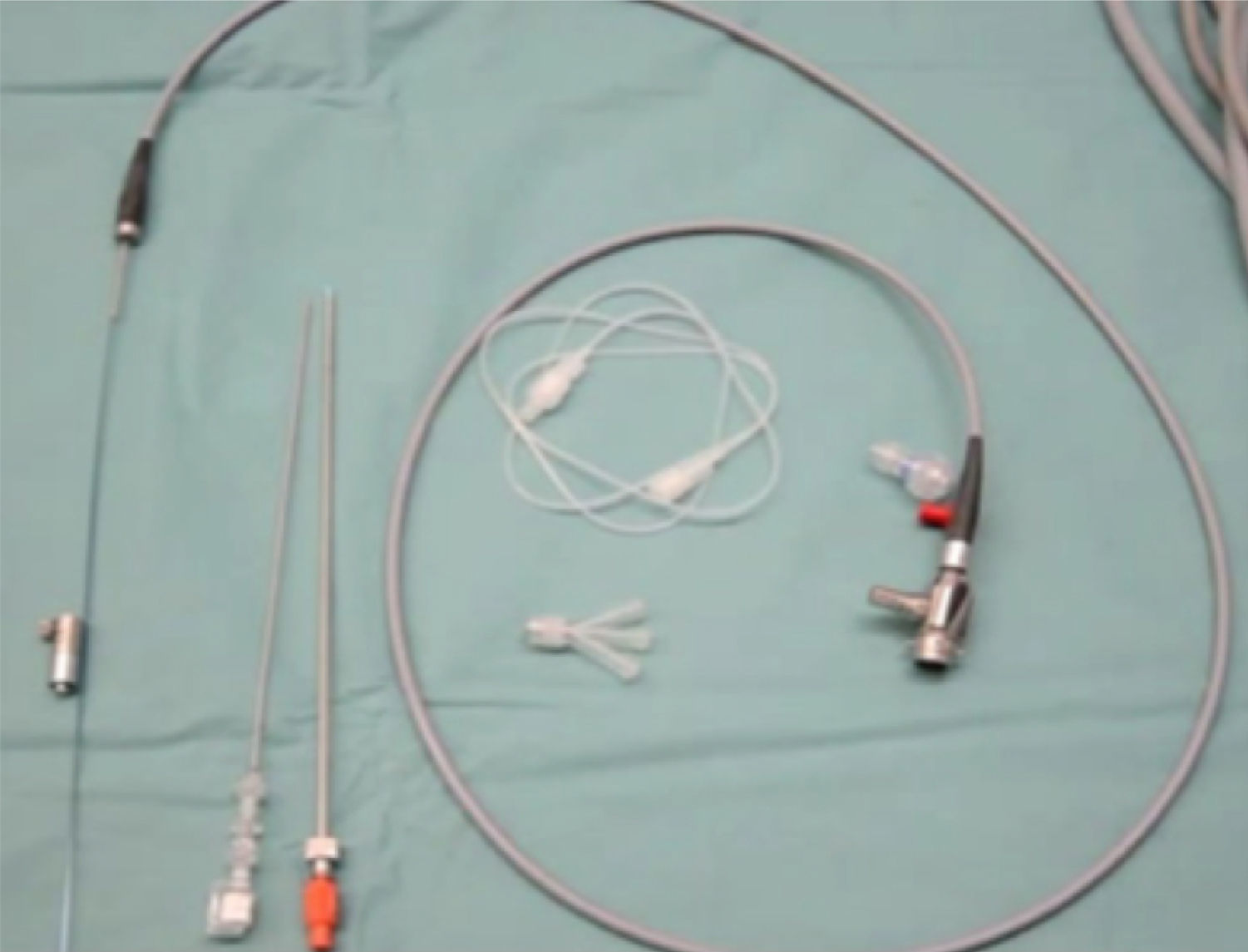
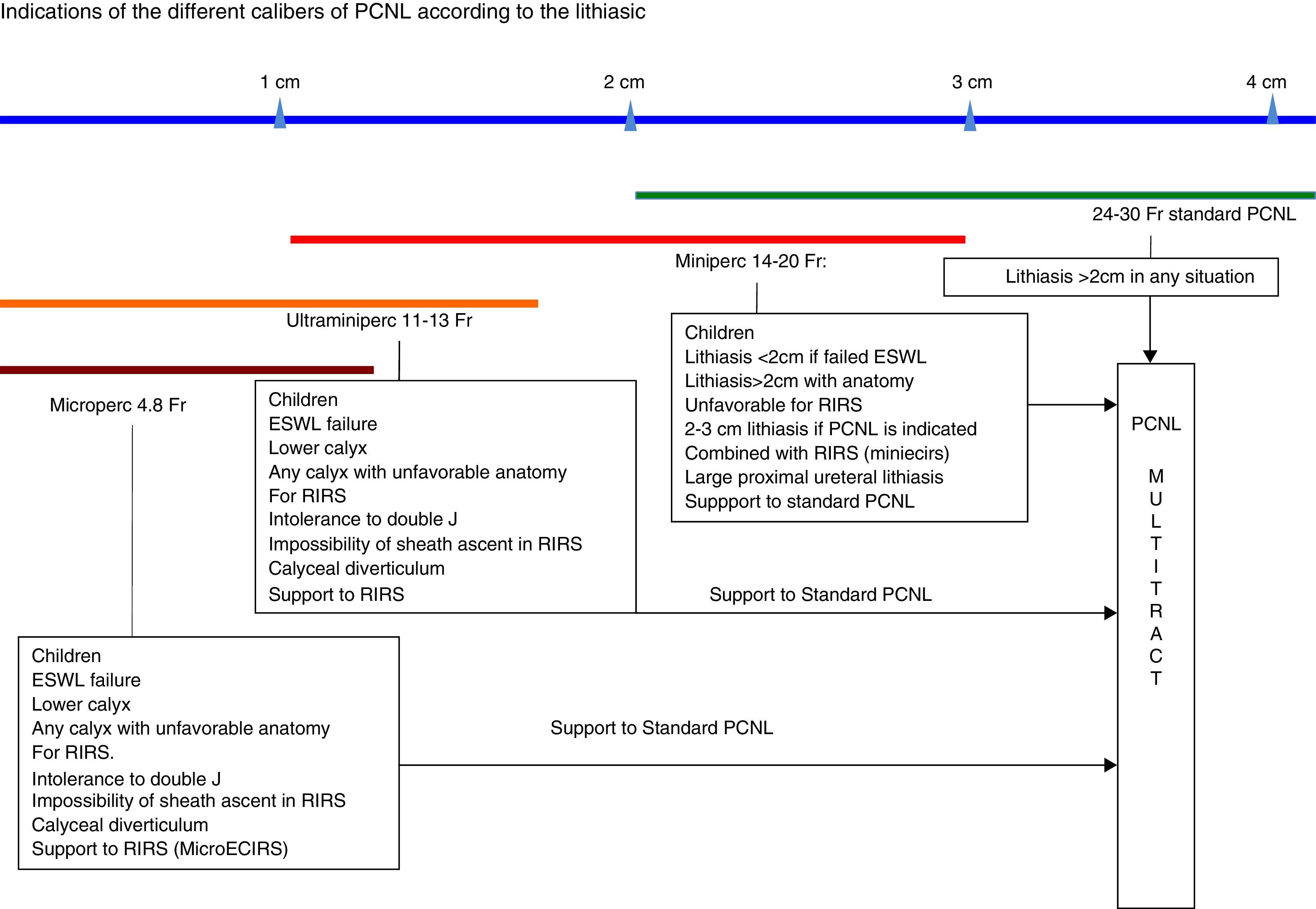
The progressive reduction in the caliber of the tract in percutaneous kidney surgery to the point of miniaturization has expanded its use to smaller stones that until now have been treated with extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS).
ObjectiveTo provide an update on the various techniques of small-caliber nephrolithotomy (SC-PCNL) analyze their efficacy, safety and indications and determine their degree of implantation at this time.
Material and methodsWe performed a review in PubMed of Spanish and English medical literature on the various techniques of SC-PCNL.
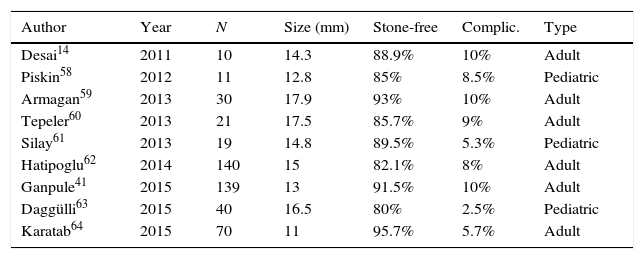
ResultsThe use of SC-PCNL has reduced the morbidity associated with standard PCNL, particularly bleeding, and has enabled tubeless nephrolithotomy with greater safety. There are various techniques with blurred terminology (Miniperc, Microperc, Mini-microperc, Ultraminiperc), which differ in terms of gauge employed and in certain technical aspects that require their indications be specified. Currently, SC-PCNL competes with techniques that are less invasive than standard PCNL such as ESWL and the RIRS in treating small stones, but the role of SC-PCNL is still not sufficiently understood and continues to be the subject of debate.
ConclusionsThe indications for PCNL are expanding to small stone sizes due to the miniaturization of the technique. PCNL competes in this field with ESWL and RIRS. Larder studies are needed to establish the specific indications for PCNL in treating nephrolithiasis.
La progresiva reducción del calibre del tracto en cirugía percutánea renal, hasta alcanzar la miniaturización, ha expandido su utilización a litiasis de menor tamaño que hasta ahora se trataban mediante litotricia extracorpórea por ondas de choque (LEOCH) y cirugía retrógrada intrarrenal (CRIR).
ObjetivoRealizar una puesta al día de las diferentes técnicas de nefrolitectomía de calibre reducido (NLP-CR) analizando su eficacia, seguridad e indicaciones, así como su grado de implantación en la actualidad.
Material y métodosRealizamos una revisión en PubMed de la literatura en castellano e inglés sobre las diferentes técnicas de NLP-CR.
ResultadosLa NLP-CR ha disminuido la morbilidad asociada a la NLP estándar, particularmente el sangrado, y ha posibilitado la nefrolitectomía tubeless con mayor seguridad. Existen diferentes técnicas con confusa terminología (miniperc, microperc, mini-microperc, ultraminiperc) que se diferencian en el calibre que emplean y en determinados aspectos técnicos que hacen que sus indicaciones deban ser precisadas. Actualmente, la NLPCR compite con técnicas menos invasoras que la NLP estándar, como la LEOCH y la CRIR en el tratamiento de las litiasis de pequeño tamaño, pero todavía su papel no está suficientemente esclarecido y es aún motivo de debate.
ConclusionesLas indicaciones de la NLP se están expandiendo a tamaños litiásicos más pequeños debido a la miniaturización de la técnica, compitiendo en este campo con LEOCH y CRIR. Precisamos mayores estudios para establecer sus indicaciones precisas en el tratamiento de la litiasis renal.