Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NC) before minimally invasive radical cystectomy (MIRC) is considered a standard of care in muscle-invasive bladder cancer or recurrent high-risk non–muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
ObjectiveTo evaluate the impact of NC on morbidity and mortality after MIRC.
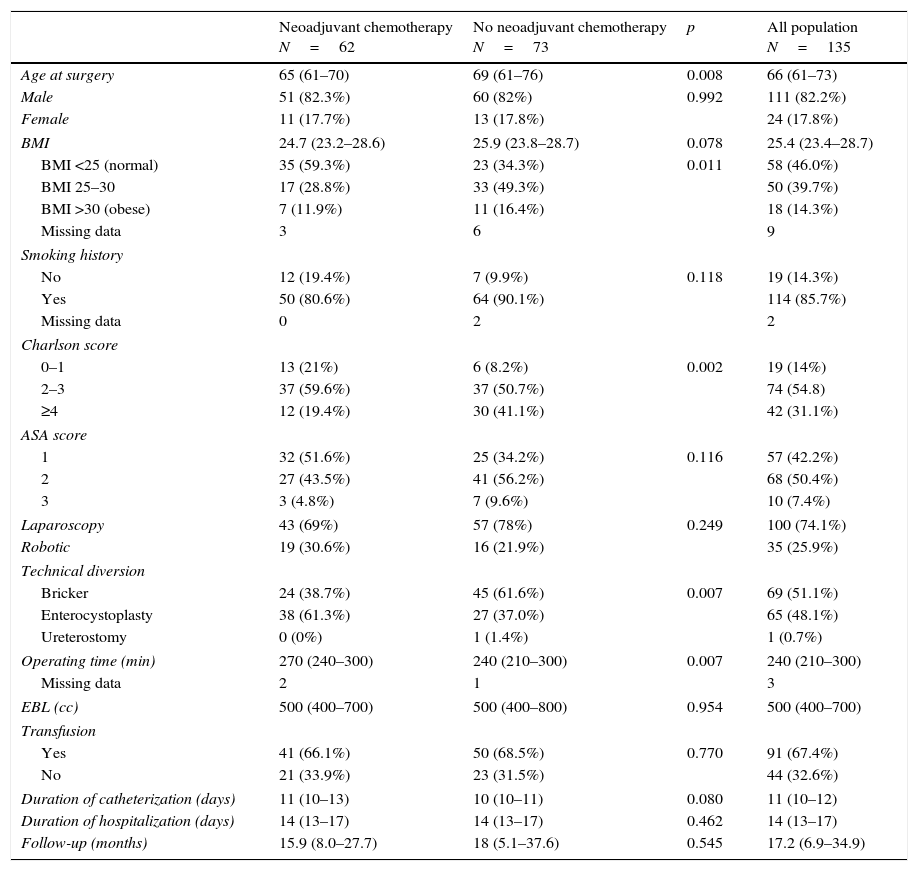
Design, setting, and participantsWe prospectively evaluated 135 patients who underwent MIRC (laparoscopic: n=100; robotic: n=35) between 2007 and 2013 with ≥90 days of follow-up (median age: 66 years). Complications were analyzed and graded according to the Clavien–Dindo classification system.
Outcome measurements and statistical analysisLogistic regression models were used to evaluate the impact of NC on postoperative complications. Kaplan–Meier methods with the log-rank test were used for cancer-specific survival probabilities and differences between the two groups (MIRC with and without NC).
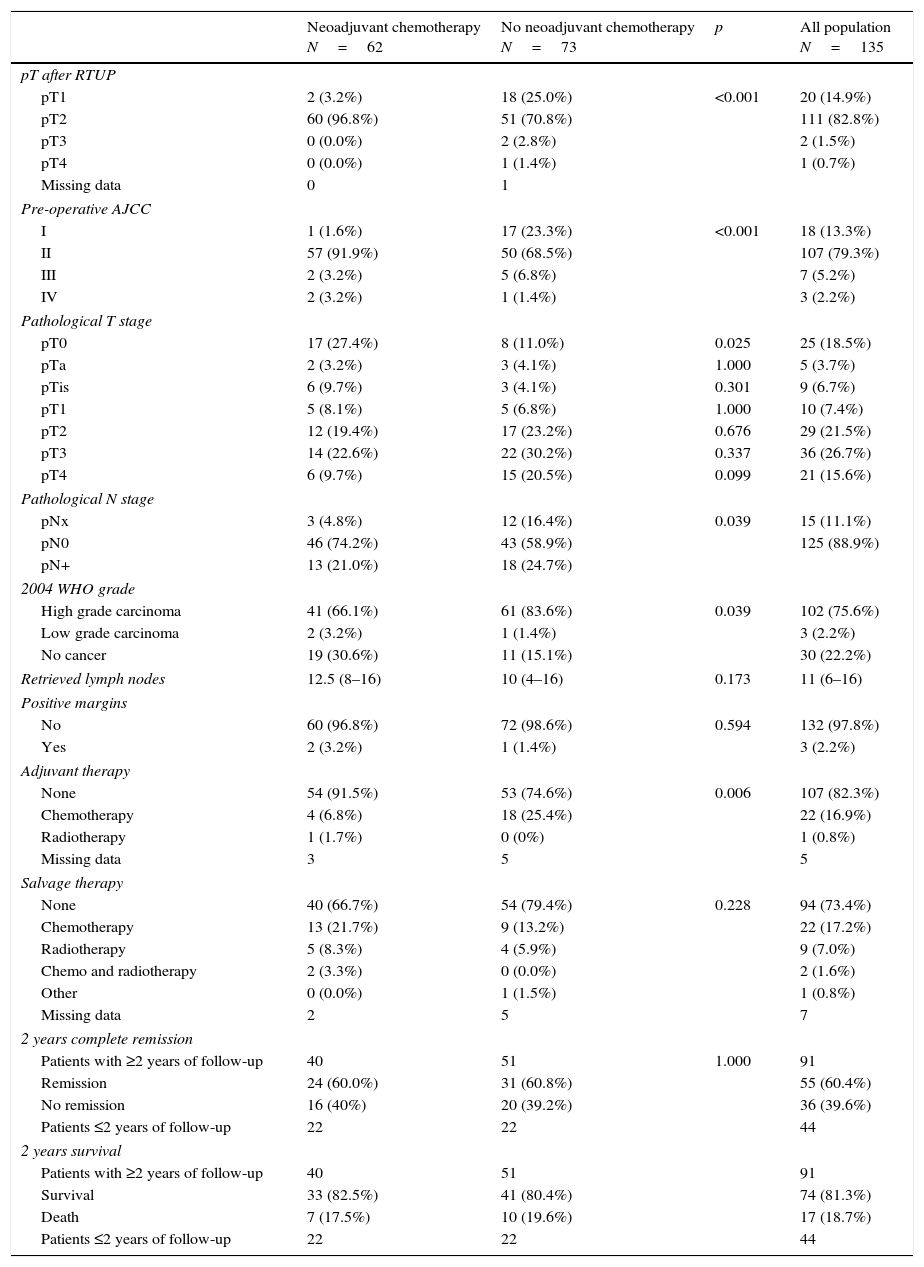
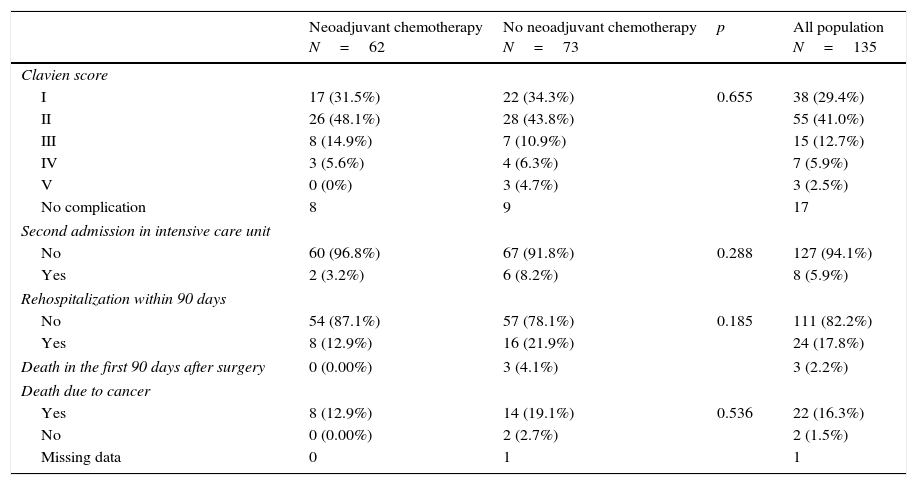
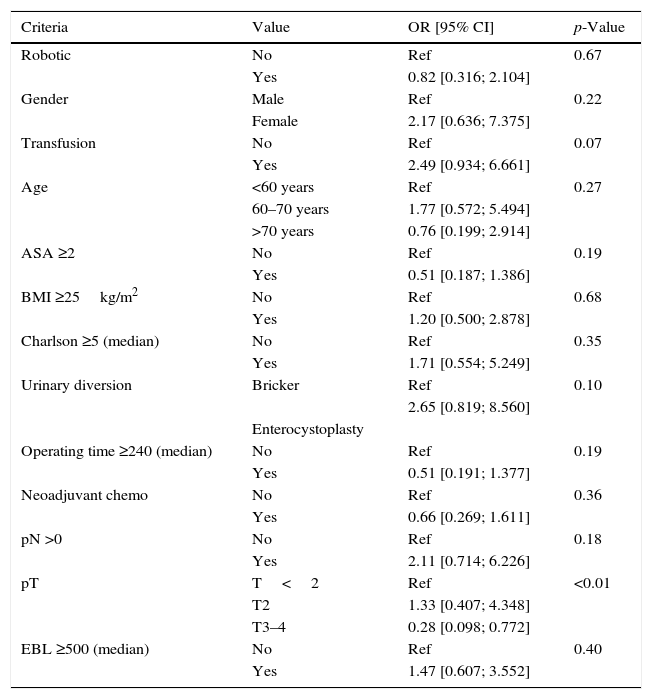
Results and limitationsSixty-two of 135 patients received NC. A total of 118 patients (87.4%) developed 179 complications, chiefly infectious (48.0%) or gastrointestinal (21.2%), ≤90 days after surgery; 3 patients died <90 days after cystectomy (none had NC). NC had no impact on the incidence of postoperative complications but was associated with fewer positive nodes (p=0.004) compared with patients without NC. The median duration of follow-up was 17.2 months. Overall survival rates were 83% and 79% at 2 years in patients with NC and without NC, respectively.
ConclusionsNC does not affect postoperative morbidity or postoperative mortality. Longer follow-up is needed to evaluate the impact of NC on oncologic outcomes.
Patient summaryPerioperative complications of radical cystectomy were compared for patients with bladder cancer who had NC vs no NC. We did not find any significant differences in terms of early or late complications, length of stay, or reintervention. The oncologic outcomes regarding NC were encouraging.
La quimioterapia neoadyuvante (QN) antes de la cistectomía radical mínimamente invasiva (CRMI) se considera un estándar de cuidado en el cáncer vesical infiltrante o cáncer vesical no músculo invasivo de alto riesgo recurrente.
ObjetivoEvaluar el impacto de la QN en la morbimortalidad después de CRMI.
Diseño, escenario y participantesSe evaluó prospectivamente a 135 pacientes intervenidos mediante CRMI (laparoscópica: n=100; robótica: n=35) entre 2007 y 2013 con ≥90 días de seguimiento (mediana de edad: 66 años). Las complicaciones fueron analizadas y clasificadas de acuerdo con el sistema de clasificación de Clavien Dindo.
Mediciones de resultados y análisis estadísticoSe utilizaron modelos de regresión logística para evaluar el impacto de la QN en las complicaciones postoperatorias. Se utilizaron métodos de Kaplan-Meier con la prueba de log-rank para las probabilidades de supervivencia específica del cáncer y las diferencias entre los 2grupos (CRMI con y sin QN).
Resultados y limitacionesDe un total de 135 pacientes, 62 recibieron QN; 118 pacientes (87,4%) desarrollaron 179 complicaciones, principalmente infecciosas (48,0%) o gastrointestinales (21,2%) ≤90 días después de la cirugía; 3 pacientes fallecieron <90 días después de la cistectomía (ninguno tenía QN). La QN no tuvo impacto en la incidencia de complicaciones postoperatorias, aunque se asoció con un menor número de ganglios positivos (p=0,004) en comparación con los pacientes sin QN. La mediana de duración del seguimiento fue de 17,2 meses. Las tasas de supervivencia globales fueron del 83 y del 79% a los 2 años en pacientes con QN y sin QN, respectivamente.
ConclusionesLa QN no afecta a la morbilidad ni a la mortalidad postoperatorias. Se necesita un seguimiento más largo para evaluar el impacto de QN en los resultados oncológicos.