To review diet risk factors (RF) implied, more or less evidence-based, in the etiopathology of prostate carcinoma (PC), especially those that characterize the traditional Mediterranean diet (MD).
Material and methodsLiterature review of PC related diet RF in MedLine, CancerLit, Science Citation Index and Embase. Search profiles were “Dietetic Factors/Nutritional Factors/Mediterranean Diet/Primary Prevention”, and “Prostate Cancer”.
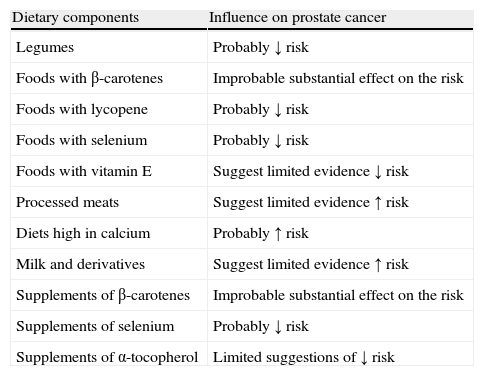
ResultsDiet RF are associated with 35% of cancer mortality and 10–12% of PC mortality. The main diet RF, implied in the development of PC but with a protective effect, which are considered characteristic of MD are: high daily ingestion of vegetarian products (cereals, legumes, dried and fresh fruits, tubercles, vegetables, etc.); olive oil as main lipid source; low intake of animal saturated fat, processed red meat, milk and dairy products; regular consumption of small fish; and low alcohol intake (wine with meals). The MD contains many phytoactive compounds (lycopene, lupeol, quercetin, genistein, carnosol, resveratrol, catechins, vitamins, etc.) with PC protective effects.
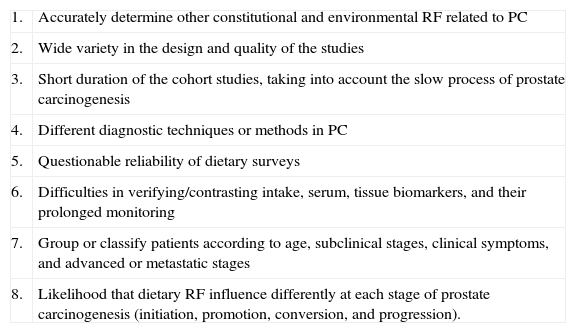
ConclusionsDiet RF have a role on prostatic carcinogenesis. Further epidemiologic studies with better designs are needed to clarify PC related diet RF. PC risk is reduced in people on MD compared with those on western diet. The common denominator of the preventive effect of the MD is based on the great quantity and quality of phytochemicals with antioxidant and antiinflamatory properties.
Revisar los factores de riesgo (FR) dietéticos implicados, con mayor o menor evidencia científica, en la etiopatogenia del carcinoma de próstata (CP), especialmente los característicos de la tradicional dieta mediterránea (DM).
Material y métodosRevisión bibliográfica de los FR dietéticos asociados al CP obtenida de MedLine, CancerLit, Science Citation Index y Embase. Los perfiles de búsqueda han sido Dietetic Factors/Nutritional Factors/Mediterranean Diet/Primary Prevention y Prostate Cancer.
ResultadosLos FR dietéticos se asocian al 35% de las muertes por cáncer y al 10-12% del CP. Los principales FR dietéticos, implicados en el CP y característicos de la DM, son los siguien-tes: ingesta diaria y elevada de alimentos vegetales (cereales, legumbres, frutas frescas-secas, tubérculos, verduras, etc.); consumo de aceite de oliva como lípido habitual; baja ingesta de grasa saturada animal, carne roja y procesada, leche y derivados; consumo regular de pescado pequeño; y escaso consumo alcohólico (vino en las comidas). La DM proporciona numerosos com-puestos fitoactivos (licopeno, lupeol, quercetina, genisteína, carnosol, resveratrol, catequinas, vitaminas, etc.) con efectos protectores del CP.
ConclusionesLos FR dietéticos influencian la carcinogénesis prostática. Para conocer con más exactitud los FR dietéticos implicados en el CP son necesarios mejores diseños epidemiológicos. La mayor adherencia a la DM, en contraste con las dietas occidentales, se asocia a menor riesgo de CP. El denominador común del efecto preventivo de la DM se basa en la gran cantidad y calidad de fitoquímicos con propiedades antioxidantes y antiinflamatorias.