Vulvodynia is a complex and multifactorial clinical condition. It is defined as chronic vulvar discomfort characterized by burning, stinging or irritation. Its diagnostic difficulty and treatment are known.
ObjectivesTo review the medical literature of the last 10 years from a critical point of view.
Evidence acquisitionA search was made in “Medline/Pubmed” and the Cochrane Library using the terms “vulvodynia” and “vestibulodynia” to which “etiology,” epidemiology, “diagnosis”, “neurophysiological test” and “treatment or management,” were added.
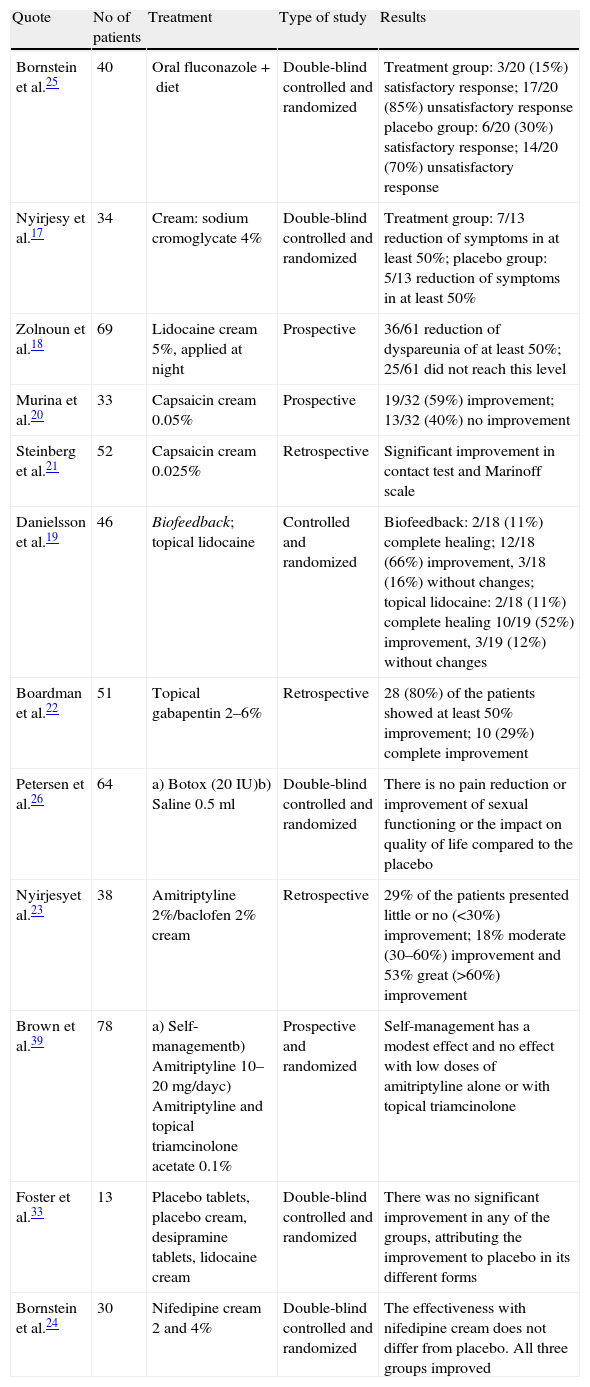
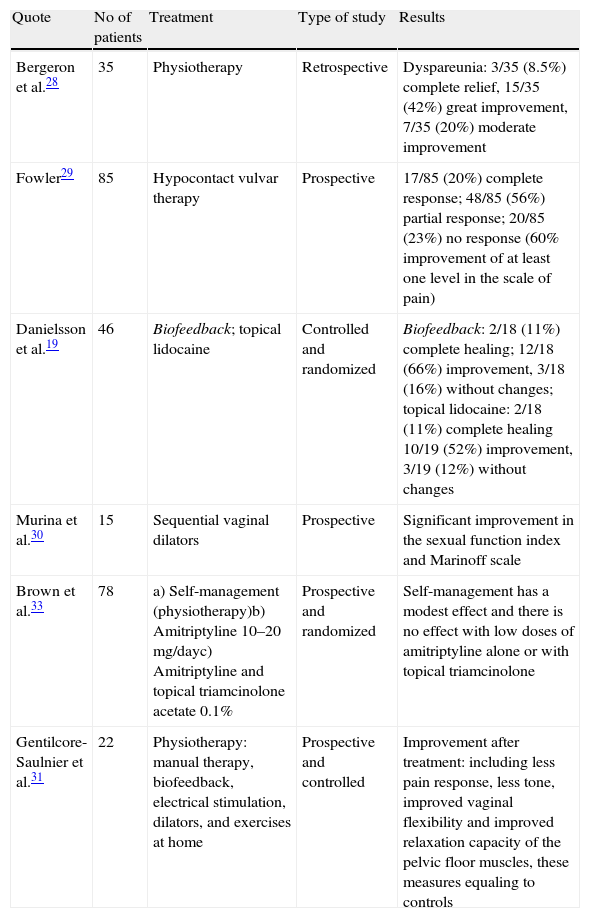
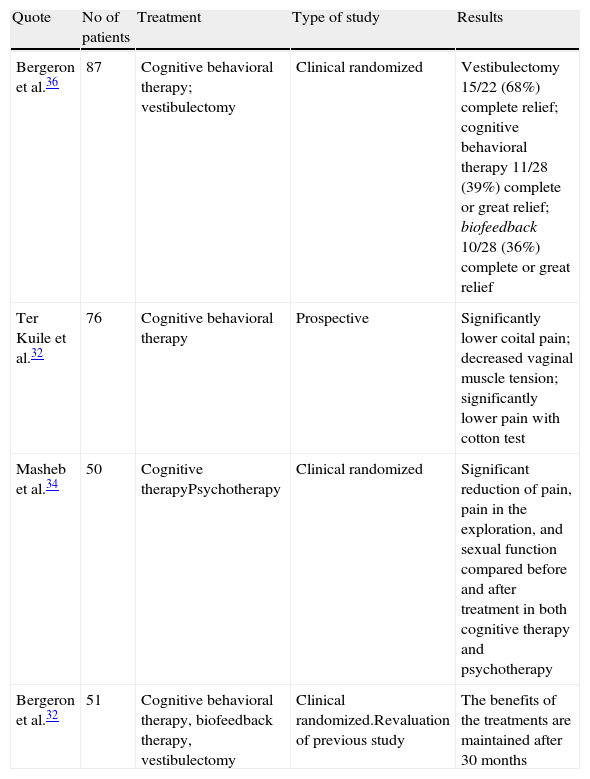
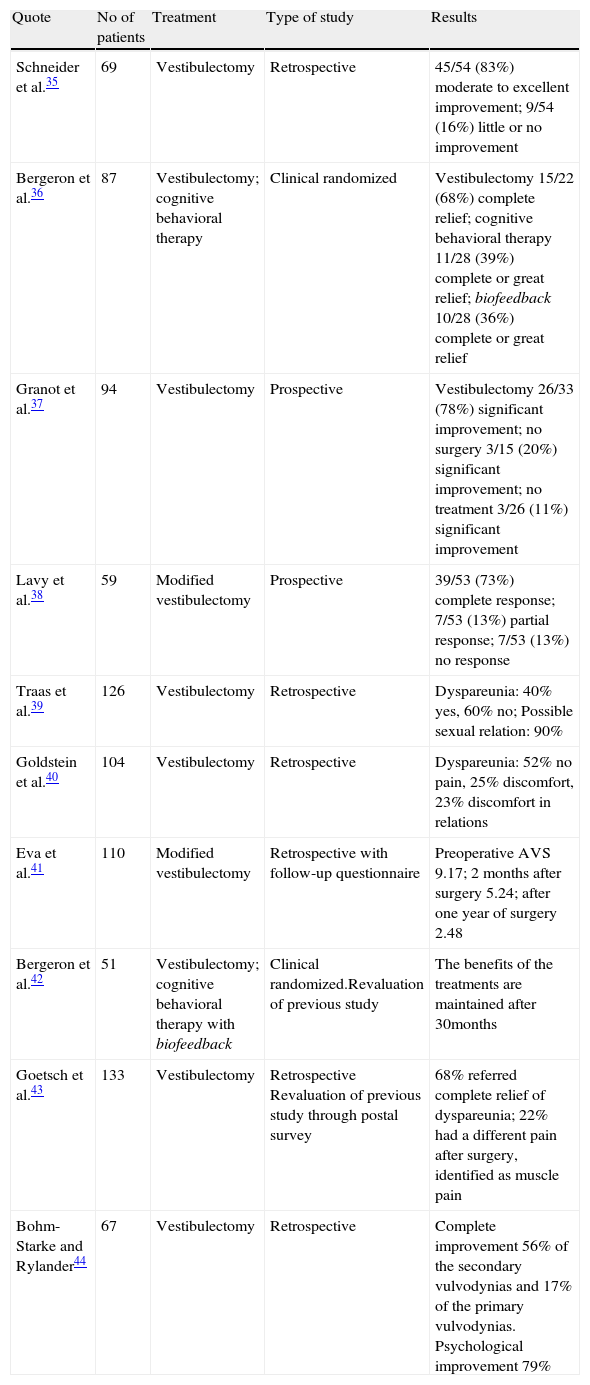
Evidence synthesisIn spite of the advances achieved in all of the aspects of vulvodynia, the methodology used at present in many cases does not have the desirable statistical soundness: there are few control or placebo-controlled groups and double-blind studies. Uniformity is lacking in the scales, indexes and questionnaires for the correct evaluation of pain before and after the treatment and debatable diagnostic criteria are used. The limited use of neurophysiological diagnostic resources that validate the clinical findings has been observed in the studies analyzed. In most of the works, the medical treatments have been shown to be ineffective. Physiotherapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy seem to be promising therapeutic tools. Surgery (vestibulectomy) stands out by its demonstrated efficacy in the publications studied.
ConclusionsA multidisciplinary approach is always necessary. Topical medical, psychological, and physical therapy treatments may have some added effects and become an alternative to surgery. New pathways of research and more regulated studies are required.
La vulvodinia es una entidad clínica compleja y multifactorial. Se define como un disconfor vulvar crónico caracterizado por quemazón, escozor o irritación. Es sabida su dificultad diagnostica y su manejo.
ObjetivosRevisar la literatura médica de los últimos diez años desde un punto de vista crítico.
Adquisición de EvidenciaSe realizo una búsqueda en “Medline/Pubmed” y librería Cochrane usando los términos “vulvodynia” y “vestibulodynia” a los que se añadieron “etiology”, “epidemiology”, “diagnosis”, “neurophysiological test” and “treatment or management”.
Síntesis de EvidenciaA pesar de los avances conseguidos en todos los aspectos de la vulvodinia, hoy, la metodología utilizada en buen número de casos no tiene la solidez estadística deseable: pocos grupos controles o placebo y estudios a doble ciego, falta de uniformidad en las escalas, índices y cuestionarios para la correcta evaluación del dolor antes y después del tratamiento y una utilización de criterios diagnósticos discutibles. Se ha visto en los estudios analizados la poca utilización de medios diagnósticos neurofisiológicos que validen los hallazgos clínicos. Los tratamientos médicos se muestran en la mayoría de los trabajos examinados poco efectivos. La fisioterapia y la terapia cognitiva -conductual parecen ser herramientas terapéuticas prometedoras. La cirugía (vestibulectomía) destaca por la eficacia demostrada en las publicaciones estudiadas.
ConclusionesEl abordaje multidisciplinar es siempre necesario. El tratamiento médico tópico, el psicológico y la fisioterapia pueden tener efectos sumatorios y convertirse en una alternativa a la cirugía. Se precisan nuevas vías de investigación y estudios más reglados.