The aim of this study was to analyze and compare the capacity of procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), lactate and leukocytes to predict the presence of bacteremia in patients with urinary tract infections (UTIs).
MethodsObservational, retro-prospective analytical study of adult patients (≥15 years) diagnosed with UTI in an emergency department from August 2012 to January 2013.
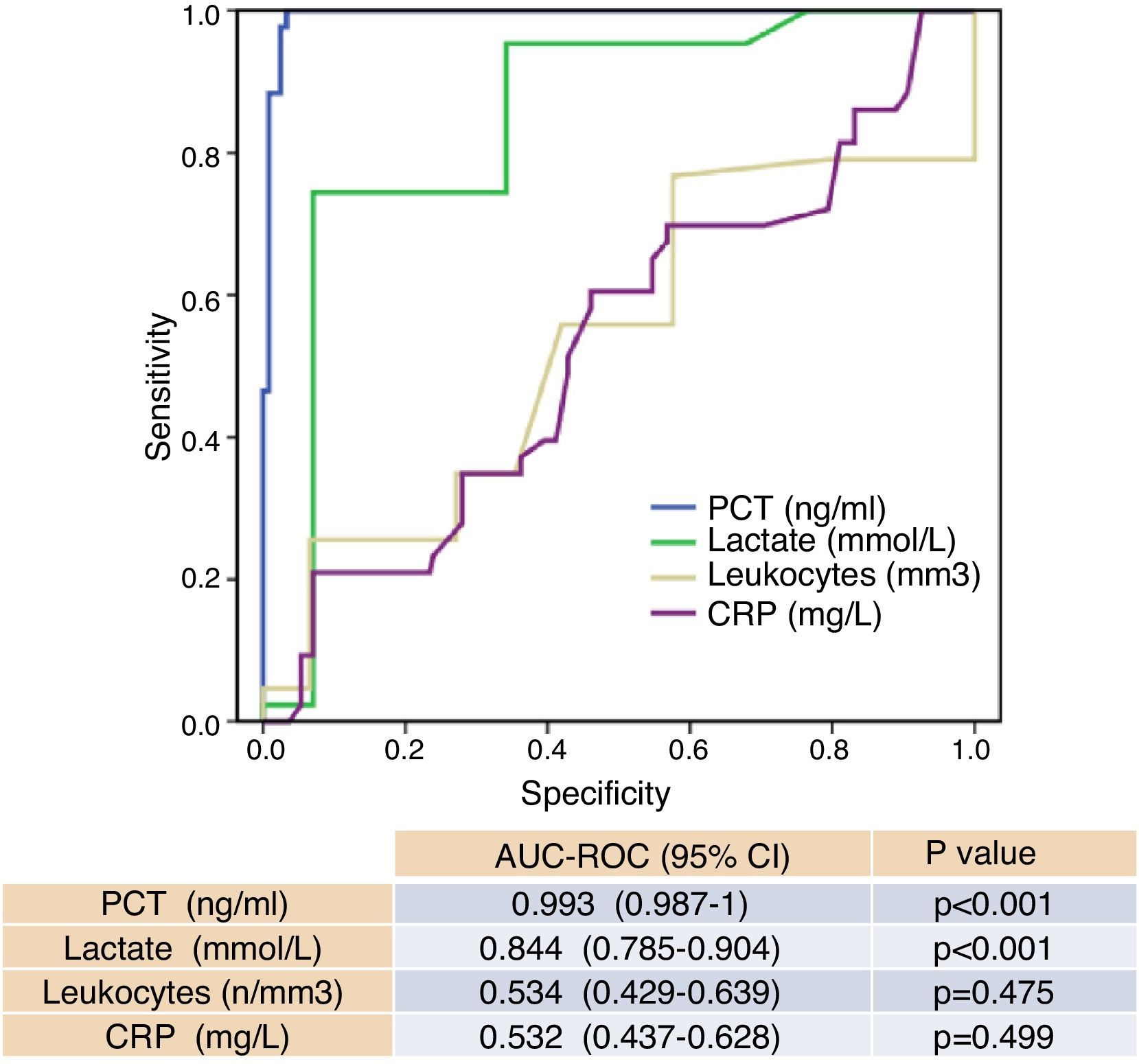
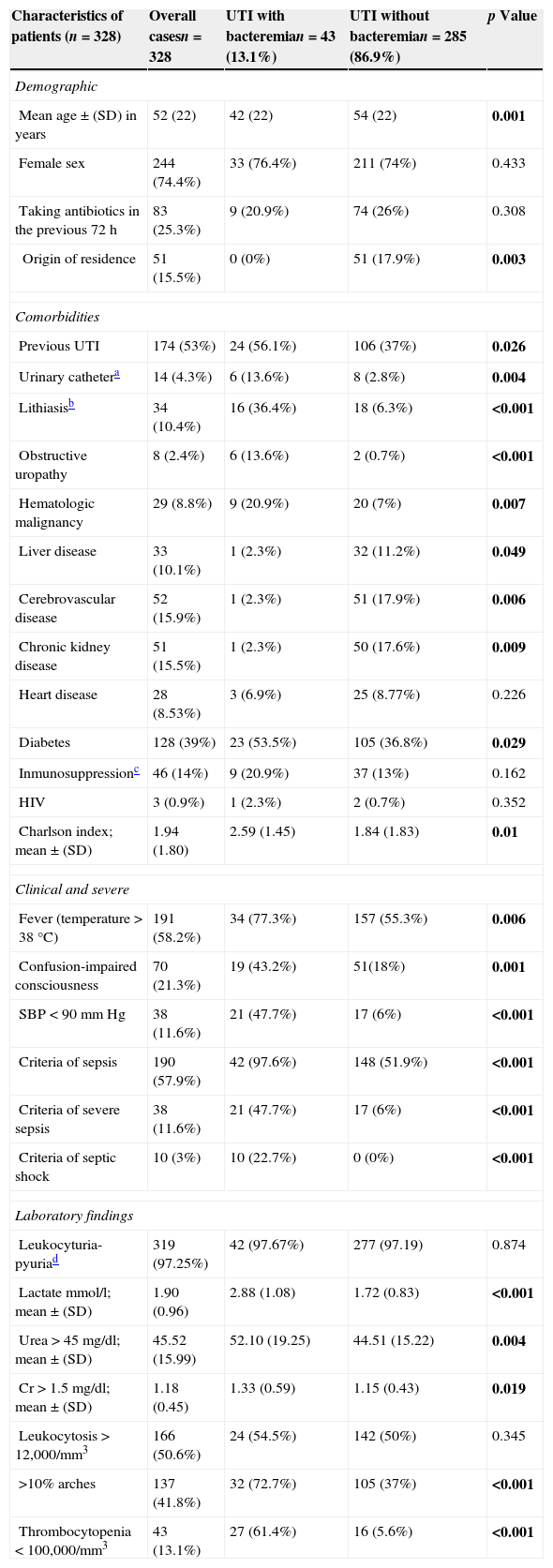
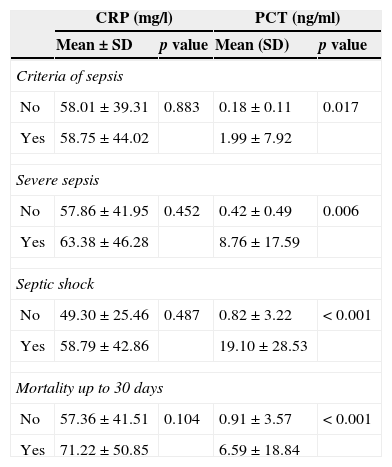
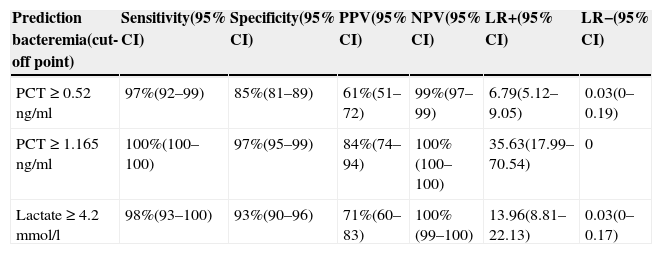
ResultsThe study included 328 patients diagnosed with UTI, with a mean age of 52±22 years, 74% of whom were women. Of these, 43 (13.1%) had bacteremia. For predicting bacteremia, PCT achieved the largest area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC–AUC) at 0.993 (95% CI: 0.987–1; p<0.001). A cutoff ≥1.16ng/ml achieves a sensitivity of 100%, a specificity of 97%, a positive predictive value of 84% and a negative predictive value of 100%. Lactate achieved an ROC–AUC of 0.844, and CRP achieved only 0.534.
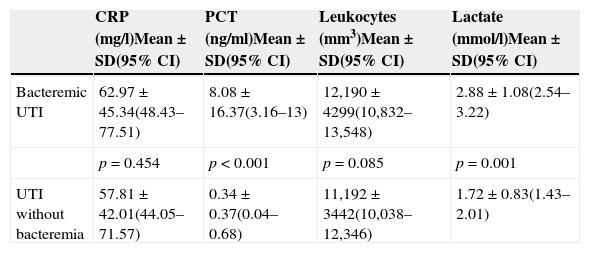
The mean values when comparing PCT levels in patients with UTIs with and without bacteremia were 8.08±16.37 and 0.34±0.37ng/ml, respectively (p<0.001).
ConclusionsFor patients with UTIs in the emergency department, PCT achieves considerable diagnostic performance for suspecting bacteremia, a performance greater than that of lactate, CRP and leukocytes.
El objetivo del estudio fue analizar y comparar la capacidad de la procalcitonina (PCT), proteína C reactiva (PCR), lactato y leucocitos para predecir la existencia de bacteriemia en los pacientes con infección del tracto urinario (ITU).
MétodosEstudio observacional, retroprospectivo y analítico de pacientes adultos (≥15 años) diagnosticados de ITU en un servicio de urgencias desde agosto de 2012 hasta enero de 2013.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 328 casos diagnosticados de ITU con una edad media de 52±22 años, el 74% mujeres. De ellos 43 (13,1%) con bacteriemia. Para predecir bacteriemia la PCT obtiene la mayor área bajo la curva ROC (ABC-ROC), de 0,993 (IC 95%: 0,987-1, p<0,001) y con un punto de corte ≥1,16ng/ml se consigue una sensibilidad del 100%, especificidad del 97%, un valor predictivo positivo de 84% y un valor predictivo negativo del 100%. El lactato consigue un ABC-ROC de 0,844 y la PCR solo de 0,534.
Los valores medios al comparar la PCT en pacientes con ITU con/sin bacteriemia fueron 8,08±16,37 vs 0,34±0,37ng/ml, p<0,001.
ConclusionesEn los pacientes con ITU en el servicio de urgencias la PCT consigue un gran rendimiento diagnóstico para sospechar bacteriemia, mayor que el lactato, la PCR y los leucocitos.