Hearing loss is a condition that affects communication and social insertion, increasing in frequency with increasing age. Explicit Health Guarantees (GES) have placed hearing loss in adults over the age of 65 years as a health priority in Chile, guaranteeing access to hearing aids to those who need it. However, it has been seen that adherence to their use is hampered by several factors.
MethodologyThis was a qualitative study to find items related to the adherence to use of hearing aids. We performed individual and focus group interviews in the Department of Otolaryngology at a hospital in Santiago (Chile) from June to September 2012.
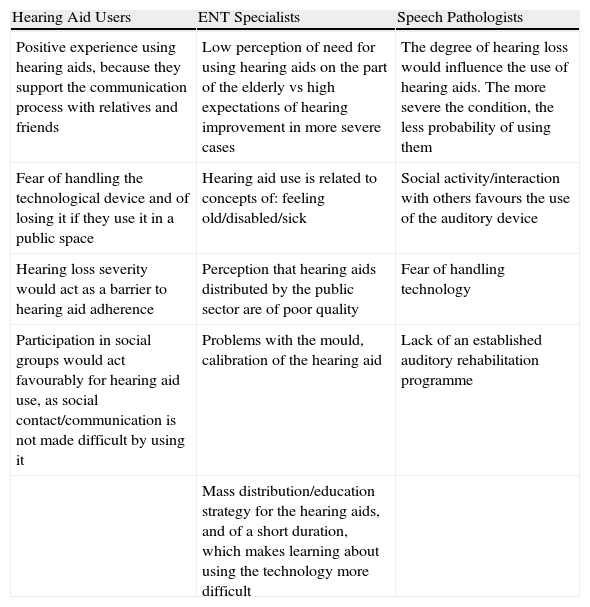
ResultsUsing hearing aids was positive for patients, perceiving an improvement in their relationship with the environment. The severity of hearing loss and the patient's own social life was relevant. For otolaryngologists and audiologists the study highlights the low patient perception of the need for hearing help. Discordance between expectations and the reality of patient adaptation is generated. Another relevant factor identified was the lack of a rehabilitation programme.
ConclusionsThe elements that influence adherence are associated with 3 groups: patient factors, audiological factors and factors dependent on the health programme. The most important, from the perspective of patients, would be the fear of improper handling; for otolaryngologists, the socio-cultural perception of the hearing aid user as a disabled individual; for audiologists, inadequate prosthetic fitting and the lack of an appropriate rehabilitation programme.
La hipoacusia es un trastorno que afecta la comunicación e inserción social, aumentando su frecuencia a mayor edad. Las garantías explícitas en salud (GES) han ubicado a la hipoacusia del adulto mayor de 65 años como una prioridad sanitaria en Chile, garantizándoles la entrega de audífonos a aquellos que lo requieran. Sin embargo, se ha visto que la adherencia a su uso se ve mermada por diversas razones.
MetodologíaEstudio cualitativo para conocer los elementos relacionados a la adherencia del uso de audífonos. Se realizó entrevistas individuales y grupos focales desde junio a septiembre de 2012, en un Servicio de Otorrinolaringología de un Hospital en Santiago, Chile.
ResultadosPara pacientes el uso de audífonos ha resultado positivo, percibiendo una mejoría en su relación con el entorno, siendo relevantes la severidad de la hipoacusia y la vida social del mismo. Para otorrinolaringólogos y fonoaudiólogos destaca la baja percepción de necesidad de ayuda auditiva por parte de los pacientes. Se genera una discordancia entre expectativas y la realidad de adaptación del paciente. Además se identifica como factor relevante la falta de un programa de rehabilitación.
ConclusionesLos elementos que influyen en la adherencia se asocian a tres grupos: factores de los usuarios, factores audiológicos, y factores dependientes del programa de salud. Los más relevantes, desde la perspectiva de usuarios serían el miedo a la incorrecta manipulación; desde los otorrinolaringólogos, la percepción sociocultural del usuario de audífono como discapacitado y los fonoaudiólogos, la inadecuada adaptación protésica y la falta de un programa de rehabilitación adecuado.