The objective of our study was to identify the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches in the different ENT Departments of Spain with respect to sudden deafness. We wanted to establish a basis to help to create a new nation-wide consensus, unifying treatment, diagnostic and follow-up criteria for this disease.
MethodsWe carried out an anonymous Internet survey, addressing Spanish ENT doctors nation-wide (n=2029), gathering in 33 questions different aspects about diagnostic criteria, additional tests, treatment procedures and prognostic factors in sudden deafness, according to the different protocols and experience of the participants in the survey.
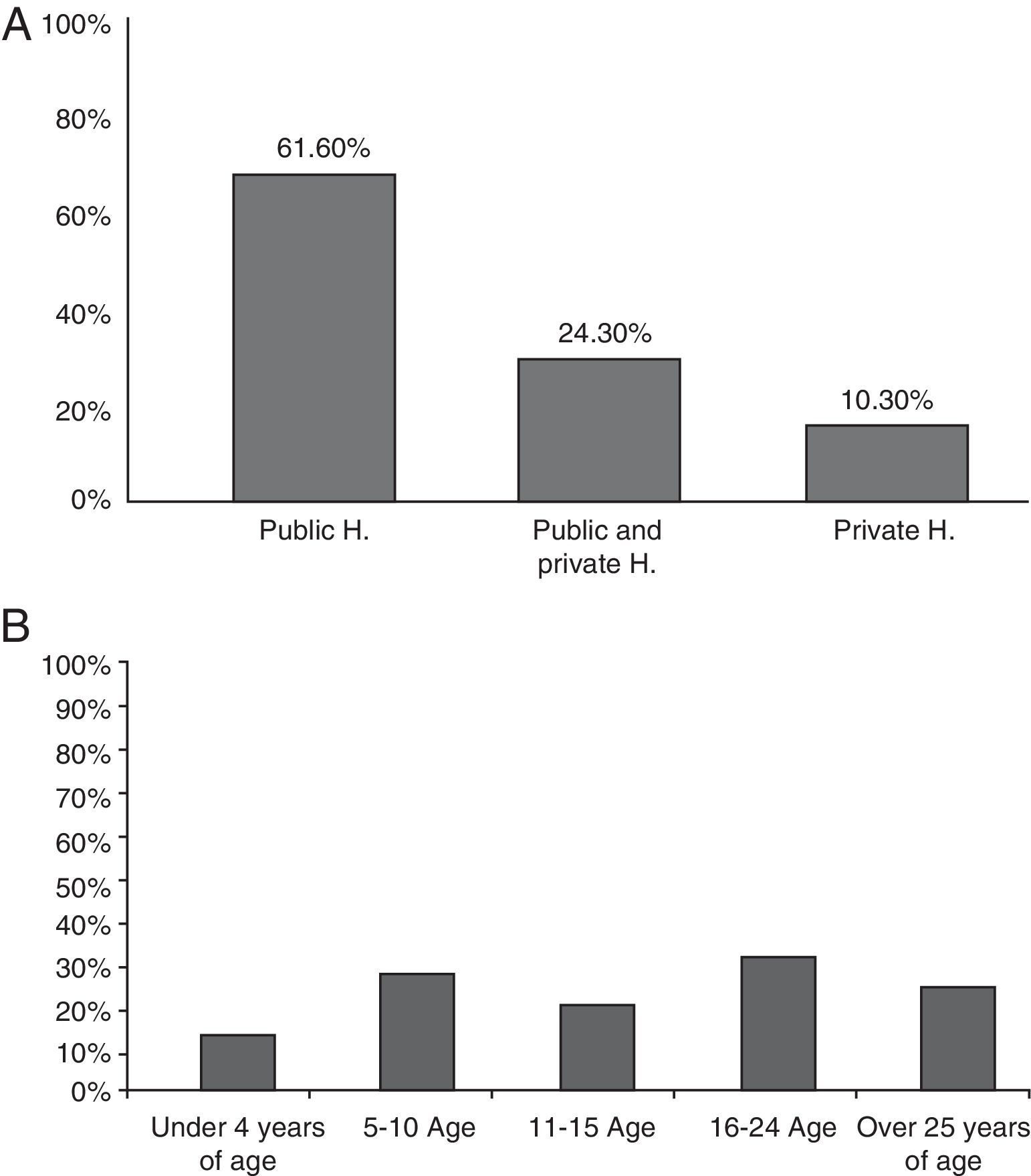
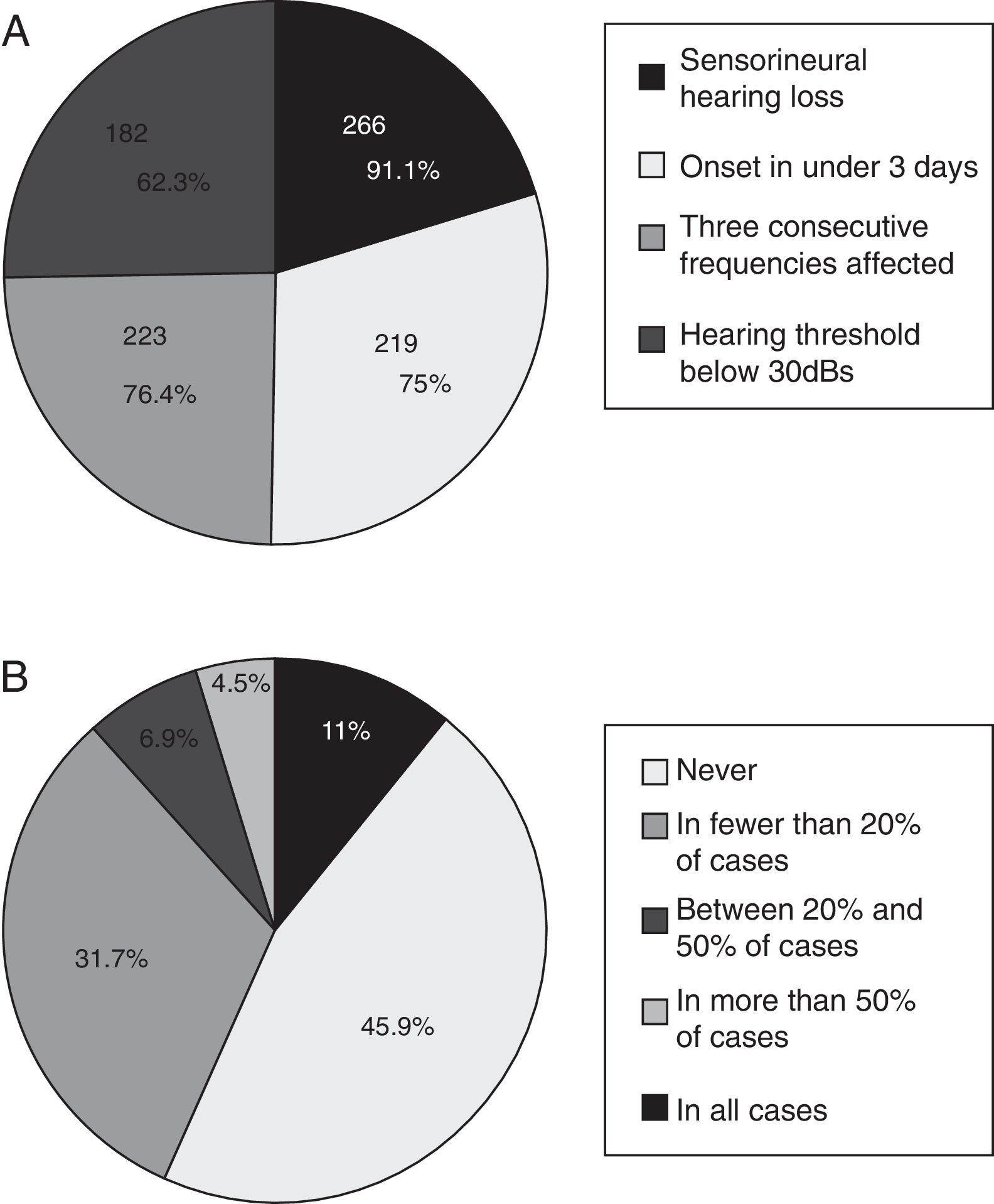
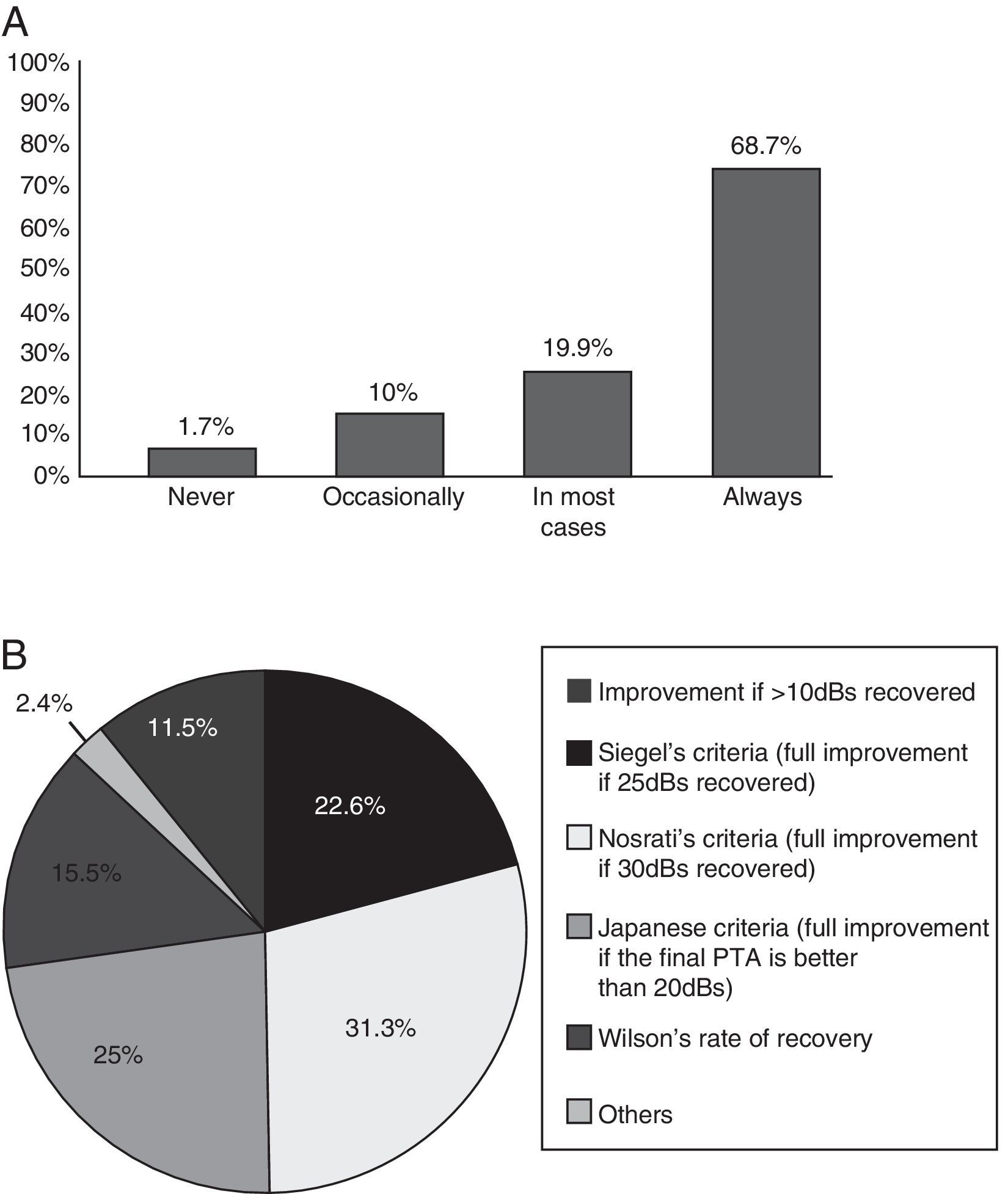
ResultsA total of 293 Spanish ENT doctors (14%) took part anonymously. In relation to diagnostic criteria, is the most noteworthy was the requisite of a confirmed neurosensorial loss (91.1%) followed by “initiated in less than three days” (75%) and 3 consecutive frequencies affected (76.4%). More than half of the participants requested an MRI of the IAC/CPA (68.7%) and 88.2% used gadolinium in this test. The prognostic factor most frequently considered was delay in commencement of treatment onset (84.8%).
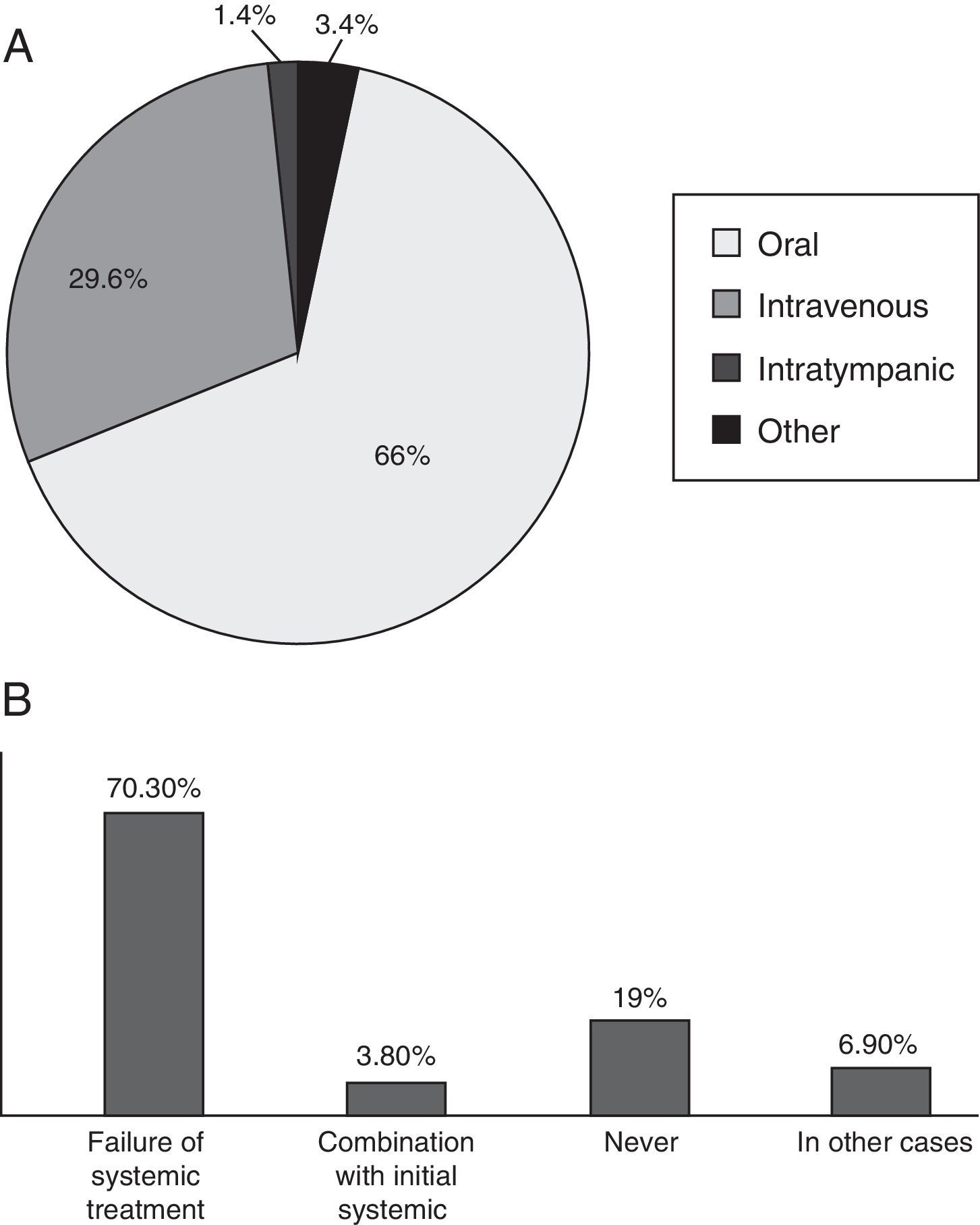
As far as treatment of primary cases, most of the responders agreed on the use of corticosteroids (99.7%). Oral administration was the most widely used (66%), followed by intravenous (29.6%) and intratympanic (1.4%) administration. Ninety-two percent had not had any major complications with systemic steroids. Intratympanic treatments were used by 70% of responders for rescue in failure.
ConclusionsIn Spain there is currently a significant disparity of concepts regarding the diagnosis of sudden deafness, and more agreement as to using steroids as their treatment. This highlights the need to implement measures to promote a better approach, which would be homogeneous and consensual, to this condition.
El objetivo de nuestro estudio es identificar las actitudes diagnósticas y terapéuticas que se llevan a cabo en los diferentes servicios de otorrinolaringología (tanto del ámbito privado como público) en España con respecto a la sordera súbita. Esto permitirá establecer una base que ayude a generar un nuevo consenso a nivel nacional, unificando criterios para el tratamiento, diagnóstico y seguimiento de esta patología.
Material y métodosSe realizó una encuesta anónima por Internet, dirigida a otorrinolaringólogos españoles a nivel nacional (n=2.029 especialistas afiliados a la SEORL), recopilando en 33 preguntas diferentes aspectos en relación a los criterios diagnósticos, pruebas complementarias, pautas de tratamiento y factores pronósticos en la sordera súbita, según los diferentes protocolos instaurados y experiencia de los participantes en la encuesta.
ResultadosParticiparon 293 otorrinolaringólogos españoles de forma anónima (14% del total). Respecto a criterios diagnósticos, destaca el requerimiento de confirmar una hipoacusia neurosensorial (91,1%), de inicio en menos de tres días (75%) y afectación de tres frecuencias consecutivas (76,4%). Más de la mitad de los participantes solicitan resonancia magnética de CAI/APC (68,7%), y el 88,2% utiliza contraste con gadolinio en esta prueba. El factor pronóstico que se consideró con mayor frecuencia en la encuesta fue la demora hasta inicio del tratamiento con un 84,8%. Respecto al tratamiento empleado en casos primarios, la gran mayoría de los encuestados (99,7%) coinciden en la administración de corticoides. La vía oral es la más utilizada (66%), seguida de la administración intravenosa (29,6%), e intratimpánica (1,4%). El 92% no han tenido complicaciones mayores con el tratamiento corticoide sistémico. La vía intratimpánica es empleada en un 70% como rescate en fracasos.
ConclusionesEn España, existe actualmente una importante disparidad en el uso de los medios diagnósticos en la sordera súbita y un mayor acuerdo en el uso de corticoides como su tratamiento. Sería necesario implementar medidas que permitan un mejor abordaje, homogéneo y consensuado de esta patología.